This article expressed by MiniTool Software Ltd. mainly introduces a type of audio data processing technology device called an audio codec. It involves the definition, comparison, conversion, examples, etc. If you are interested in this topic, just read on!
What Is an Audio Codec?
An audio codec refers to a hardware device or software application that is able to encode or decode a digital data stream in type of audio or sound. The audio codec that can encode an audio stream and create audio files is called an audio encoder such as a sound recorder. Whereas the codec that can decode an audio stream and play audio files is named an audio decoder like a music player. To make it simpler, an audio codec is the share name of an audio encoder and audio decoder.
Hardware Audio Codec
In the physical hardware field, an audio codec stands for a device that encodes analog audio as digital signals and decodes digital signals back to analog. It consists of both an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) running off the same clock signal.
That is applied in sound cards that support both audio in and audio out. Audio codec hardware sends and receives digital data relying on USB buses like AC-Link, I2S, Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI), Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C), and so on.
Usually, the digital data signal is linear Pulse-code modulation (PCM), which is the only audio codec format that most audio codecs are compatible with. Yet, some legacy audio codecs support other formats, G.711 for telephony for example.
Software Audio Codec
A software audio coder implements an algorithm that compresses (encodes) and decompresses (decodes) digital audio data based on a given audio file or streaming media coding format. The algorithm aims to represent the high-fidelity audio signal with minimum file size while retaining audio quality.
That can greatly save the storage space and the bandwidth needed to transfer the compressed audio. Most modern audio compression algorithms are based on modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) coding and linear predictive coding (LPC). Besides, most software codecs are implemented as libraries that interface to at least one media player.
Compare Audio Coding Formats
To compare different audio coding formats, engineers or technicians may take their supported operating systems (OSes), supported multimedia frameworks, adopted technologies, as well as general specifications into consideration.
Next, let’s see the specific aspects that need to compare among various audio codecs.
# Supported OS
In general, most audio codec formats are designed to be applied to these operating systems, including computer systems and mobile phone OSes.
# Supported Multimedia Frameworks
Next, let’s have a look at what software apps are usually taken as the standards for estimating the audio player support.
- Audio Compression Manager (for Windows)
- DirectShow (for Windows)
- Media Foundation (for Windows including Windows 11/10/8/7)
- QuickTime (for macOS)
- GStreamer (for multiple systems)
- FFmpeg (for various systems)
# Supported Technologies
As for comparing the audio codec formats’ technologies, first of all, we need to sort those codecs into different groups that will be compared with different technical parameters.
Lossy Audio Codec Formats
Lossy audio codecs are coding formats that will lose some information after encoding/compressing the audio data. For this kind of codec, we usually estimate the following technical details.
- Codec algorithm
- Sample rate
- Bitrate
- Constant bit rate (CBR)
- Variable bit rate (VBR)
- Latency
- Stereophonic sound
- Multichannel (surround sound)
Lossless Audio Codec Formats
On the contrary, lossless audio codecs are coding formats that won’t lose any quality after compression compared to the original audio file. The below technologies will be compared when choosing a proper lossless audio encoder. Most of the aspects are the same as those of lossy video sound codecs.
- Coding algorithm
- Sample rate
- Bits per sample
- Latency
- Stereo
- Multichannel
ITU-T formats
The following will list the comparison items for audio encoders/decoders belonging to ITU-T standards.
- Comparison algorithm
- Sample rate
- Bitrate
- Bits per sample
- Constant bit rate (CBR)
- Variable bit rate (VBR)
- Latency
- Stereo
- Multichannel (surround sound)
How to Convert Audio Codec?
After learning the comparison standards of different audio codecs, you may figure out your favorite audio coding formats. If your current videos are not of the audio codes you like, you can change it to the one you prefer with a professional and reliable audio codec converter – MiniTool Video Converter, which can easily and quickly alter audio and video encoders for free.
MiniTool Video ConverterClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
1. Download, install, and open MiniTool Video Converter on your computer.
2. Go to the Converting subtab under the main Video Convert tab to add your audio file(s).
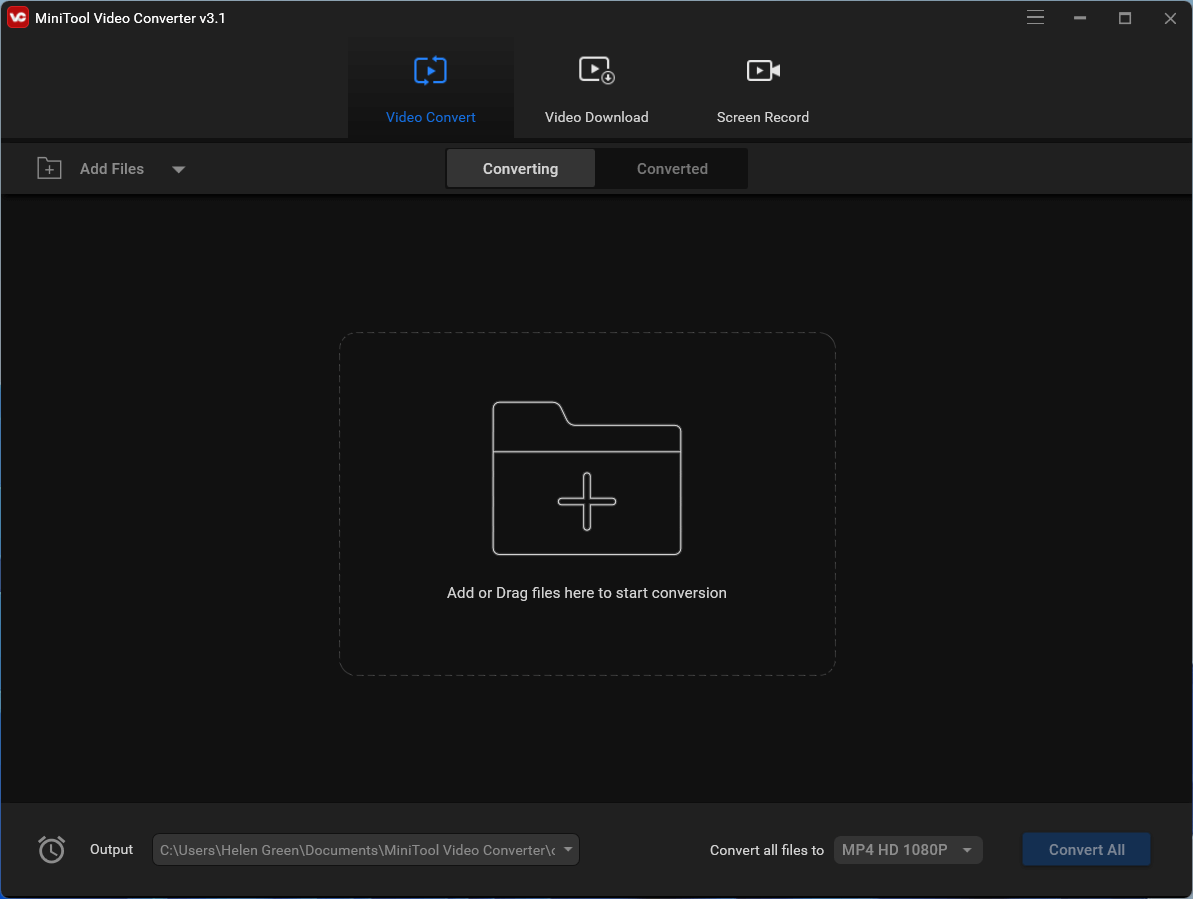
3. Then, click the editing icon in the Target section on the audio file.
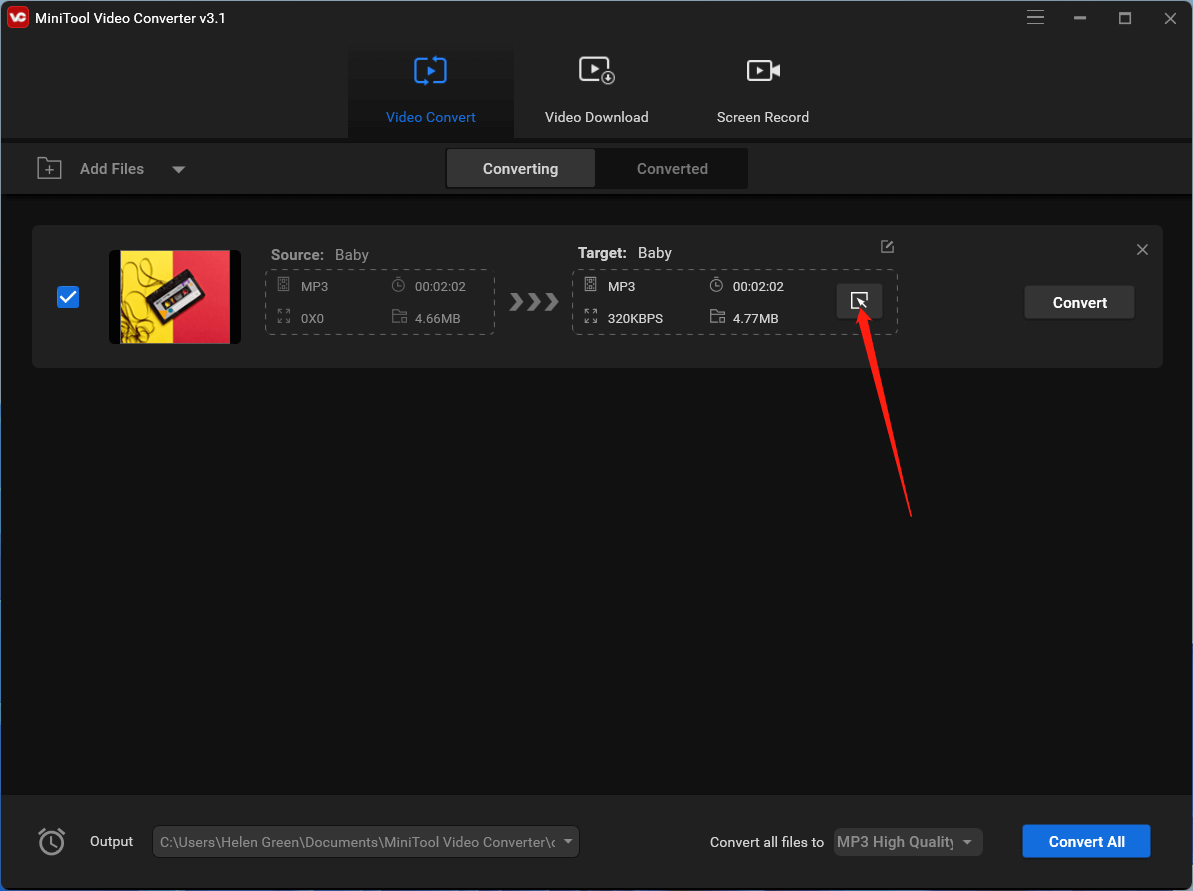
4. In the pop-up editing window, move to the Audio tab. There, select your favorite audio format from the left menu and choose a quality in the right section or directly click the Create Custom option in the lower right part.
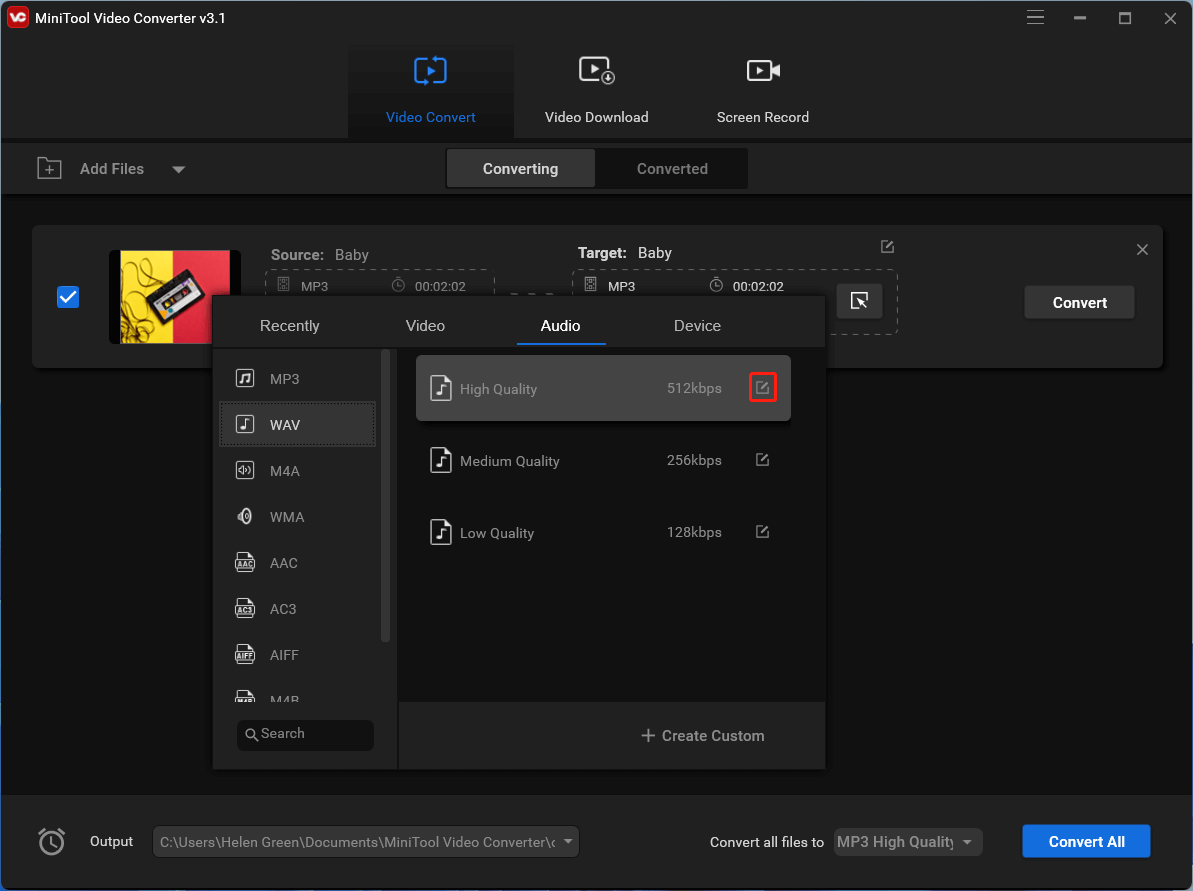
5. To check your new audio codec, you need to click on the editing icon behind the quality you choose. If you select Create Custom in the last step, you will be directly shown the audio settings window.
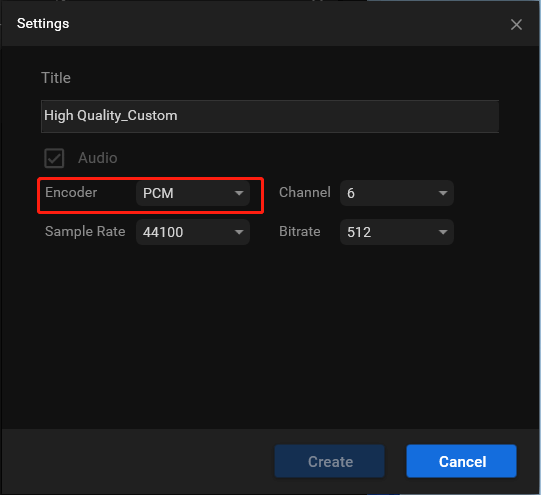
6. There, you can change other parameters of your audio like channel, sample rate, and bitrate. If you make some changes, remember to click the Create button to save them.
7. Back to the audio format selection window, just choose your customized audio that appears after you click the Create button above.
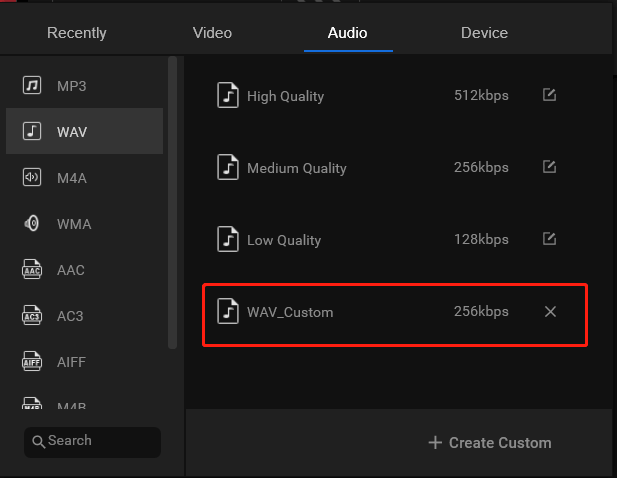
8. Finally, click on the Convert button on the audio file to begin the process.
In addition to audio codec format conversion, MiniTool Video Converter can also record a video (with audio) of different file formats including WMV, MKV, AVI, MOV, FLV, MP4, and TS, all encoded by H.264. Moreover, it can download songs and videos from YouTube in different formats like MP3, MP4, WEBM, WAV, etc.
Audio Formats/Codecs List
Here in this part, we will collect the lists of audio compression formats and their related codecs. Generally, the audio encoder formats can be divided into three categories: non-compression audio formats, lossless audio compression formats, and lossy audio compression formats.
Non-Compression Audio Formats
Linear pulse-code modulation (LPCM)
- FFmpeg
Pulse-density modulation (PDM)
- Direct Stream Digital (DSD): foobar2000 Super Audio CD Decoder, FFmpeg
Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM)
Lossless Compression Audio Formats
Actively used
Most popular
- Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC): libFLAC, FFmpeg
- Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC): Apple QuickTime, libalac, FFmpeg, Apple Music
- Monkey’s Audio (APE): Monkey’s Audio SDK, FFmpeg
- OptimFROG (OFR)
- Tom’s verlustfreier Audiokompressor (TAK): TAK SDK, FFmpeg
- WavPack (WV): libwavpack, FFmpeg
- True Audio (TTA): libtta, FFmpeg
- Windows Media Audio Lossless (WMAL): Windows Media Encoder, FFmpeg
Other
- DTS-HD Master Audio (also DTS++ and DCA XLL): libdca, FFmpeg
- Dolby TrueHD: FFmpeg
- Meridian Lossless Packing (MLP), also known as Packed PCM (PPCM): FFmpeg
- MPEG-4 Audio Lossless Coding (MPEG-4 ALS): SSC, DST, ALS and SLS reference software, FFmpeg
- MPEG-4 Scalable Lossless Coding (MPEG-4 SLS): SSC, DST, ALS and SLS reference software
- RealAudio Lossless: RealPlayer, FFmpeg
- BFDLAC (BFD Lossless Audio Compression): FXpansion’s BFD3 drum software
Oddball
- ATRAC Advanced Lossless (AAL): FFmpeg
- Direct Stream Transfer (DST): SSC, DST, ALS and SLS reference software, FFmpeg
- Original Sound Quality (OSQ)
Discontinued
- Lossless Audio (LA)
- Shorten (SHN): libshn, FFmpeg
- Lossless Predictive Audio Compression (LPAC)
- Lossless Transform Audio Compression (LTAC)
- MPEG-1 Audio Layer III HD (mp3HD)
- RK Audio (RKAU)
Bluetooth lossless
- aptX Lossless
Lossy compression
- Discrete cosine transform (DCT): Modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT)
General/Speech hybrid
Unified Speech and Audio Coding (USAC, MPEG-D Part 3)
IETF standards
- Opus: libopus, FFmpeg
IETF Internet Draft
- IPMR Speech Codec
General
Adaptive differential pulse-code modulation (ADPCM, also called adaptive delta pulse-code modulation)
Adaptive Transform Acoustic Coding (ATRAC)
- FFmpeg
ATSC/ETSI standards
- Dolby Digital: FFmpeg, liba52
- Dolby Digital Plus: FFmpeg
- DTS Coherent Acoustics (DTS, Digital Theatre System Coherent Acoustics): FFmpeg, libdca
- Dolby AC-4
Impala Blackbird audio codec
ITU standards
- 719
- 722: FFmpeg
- 722.1 and G.722.1 Annex C: libg722_1, libsiren
- 722.2: 3GPP, opencore-amr, VisualOn AMR-WB encoder, FFmpeg
- EVS
MPEG-1 Audio and MPEG-2 Audio
- layer I (MP1) (MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and non-ISO MPEG-2.5): FFmpeg
- layer II (MP2) (MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and non-ISO MPEG-2.5): FFmpeg, tooLame, twoLame
- layer III (MP3) (MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and non-ISO MPEG-2.5): FFmpeg, LAME
- Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) (MPEG-2 Part 7): FAAC and FAAD, FFmpeg, iTunes, Nero AAC Codec, VisualOn AAC Encoder (a.k.a. libvo_aacenc), Fraunhofer FDK AAC, libaacplus
MPEG-4 Audio
- Advanced Audio Coding (AAC, MPEG-4 Part 3 subpart 4), HE-AAC and AAC-LD: FAAC, FAAD2, FFmpeg, iTunes, Nero AAC Codec, MPEG-4 AAC reference software
- Harmonic and Individual Lines and Noise (HILN, MPEG-4 Parametric Audio Coding): MPEG-4 reference software
- TwinVQ: MPEG-4 reference software, FFmpeg
- BSAC (Bit-Sliced Arithmetic Coding): MPEG-4 reference software
MPEG-H
- MPEG-H 3D Audio
Musepack (a.k.a. MPEGplus)
- Musepack SV8 Tools
- FFmpeg
NICAM
AT&T Perceptual Audio Coder
Precision Adaptive Subband Coding (PASC)
QDesign
- QDesign Music Codec: FFmpeg
PictureTel
- Siren 7: libg722_1, libsiren, FFmpeg
- Siren 14: libg722_1, vgmstream
- Siren 22
NTT TwinVQ
- FFmpeg
- NTT TwinVQ Encoder, NTT TwinVQ Player
Voxware MetaSound
- Windows Media Player (voxmsdec.ax)
- FFmpeg
Vorbis
- aoTuV
- FFmpeg
- libvorbis
- Tremor
Windows Media Audio (WMA)
- Windows Media Encoder
- FFmpeg
AES3
SMPTE 302M
- FFmpeg
Dolby E
- FFmpeg
Bluetooth audio codec
Bluetooth Special Interest Group
- Low Complexity Subband Coding (SBC): BlueZ’s SBC library (libsbc), Fluoride Bluetooth stack, FFmpeg
- CVSD 8 kHz
- modified SBC (mSBC): BlueZ’s SBC library (libsbc), Fluoride Bluetooth stack, FFmpeg
- LC3 (Low Complexity Communication Codec)
ETSI
- LC3plus
Qualcomm Technologies International (formerly CSR)
- aptX (a.k.a. apt-X): Qualcomm libaptX, FFmpeg
- aptX HD: Qualcomm libaptXHD, FFmpeg
- aptX Low Latency
- aptX Adaptive
- FastStream
Sony
- LDAC: libldac
HWA Alliance/Savitech
- LHDC: HWA encoder/decoder
- LLAC: HWA encoder/decoder
HiBy
- Ultra Audio Transmission (UAT)
Samsung
- Samsung HD/UHQ-BT codec
- Samsung Scalable codec
Digital radio
Hybrid Digital Coding
- NRSC-5 receiver for rtl-sdr
Voice
Linear predictive coding (LPC)
- Code-excited linear prediction (CELP): Algebraic code-excited linear prediction (ACELP)
Xiph.Org Foundation
- Speex, patent free: libspeex, FFmpeg
Dialogic ADPCM (VOX)
- FFmpeg
ITU standards
- 711: Sun Microsystems’ public domain implementation, FFmpeg (libavcodec)
- 711.0 (G.711 LLC)
- 711.1
- 711.1D
- 718 (8/12/16/24/32kbit/s)
- 718B
- 719
- 721: Sun Microsystems’ public domain implementation
- 722 (SB-ADPCM; 48/56/64kbit/s): FFmpeg
- 722B
- 722.2 (AMR-WB): 3GPP, opencore-amr, FFmpeg
- 723: Sun Microsystems’ public domain implementation
- 723.1: FFmpeg
- 726 (ADPCM; 16/24/32/40kbit/s): Sun Microsystems’ public domain implementation, FFmpeg
- 727: Sun Microsystems’ public domain implementation
- 728 (LD-CELP; 16kbit/s)
- 729 (CS-ACELP; 8kbit/s): FFmpeg
- 729a
- 729b
- 729ab
- 729d (6.4kbit/s): FFmpeg
- 729e (11.8kbit/s)
- 729.1
- 729.1E
- Internet Speech Audio Codec (iSAC): WebRTC
- Lyra (codec)
Nellymoser Asao Codec
- FFmpeg (libavcodec)
PictureTel PT716, PT716plus
PictureTel PT724
RTAudio
SVOPC
OpenLPC
- HawkVoice (libHVDI)
ANSI/SCTE
- ANSI/SCTE 24-21 2006 (BroadVoice16): BroadVoice Speech Codec Open Source C Code
- ANSI/SCTE 24-22 2013 (iLBCv2.0)
- ANSI/SCTE 24-23 2007 (BroadVoice32): BroadVoice Speech Codec Open Source C Code
IETF RFCs
- Internet Low Bit Rate Codec (iLBC, RFC 3951): WebRTC
IETF Internet Draft
- SILK
- CELT: libcelt
MPEG-4 Audio
- MPEG-4 CELP
- MPEG-4 HVXC
Skyphone MPLP
Inmarsat
- INMARSAT-M IMBE
- Inmarsat Mini-M AMBE
Satin
Microsoft DirectPlay
These codecs are used by many PC games which use voice chats via Microsoft DirectPlay API.
Voxware MetaVoice
- Windows Media Player (voxmvdec.ax)
Truespeech
- Windows Media Player (tssoft32.acm)
- FFmpeg
MS GSM
- Windows Media Player (msgsm32.acm)
- libgsm
- FFmpeg
MS-ADPCM
- Windows Media Player (msadp32.acm)
- FFmpeg
Digital Voice Recorder
International Voice Association (IVA) standards
- Digital Speech Standard / Standard Play (DSS-SP): FFmpeg
- Digital Speech Standard / Quality Play (DSS-QP)
Sony LPEC
Truespeech Triple Rate CODER (TRC)
Mobile phone
Generation 2
- European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) GSM: Full Rate (libgsm/FFmpeg), Half Rate, Enhanced Full Rate
- Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) IS-95 (a.k.a. cdmaOne): IS-96A (QCELP 8kbit/s), IS-127 (EVRC 8kbit/s), IS-733 (QCELP 13kbit/s)
- Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) IS-54/IS-136 (a.k.a. Digital AMPS): IS-85 (VSELP 8kbit/s), IS-641 (ACELP 7.4kbit/s)
- Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (ARIB) RCR STD-27 (PDC): PDC-HR (PSI-CELP 3.45kbit/s), PDC-FR (VSELP 11.2kbit/s), PDC-EFR CS-ACELP 8kbit/s (a.k.a. G.729), PDC-EFR ACELP 6.7kbit/s
Generation 3/4
1) 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)
Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR)
- AMR-NB: 3GPP, opencore-amr, FFmpeg
- AMR-WB: 3GPP, opencore-amr, vo-amrwbenc, FFmpeg
- AMR-WB+: 3GPP
- Enhanced Voice Services (EVS): 3GPP
2) 3rd Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP2)
- Enhanced Variable Rate Codec (EVRC, a.k.a. IS-127): FFmpeg
- Enhanced Variable Rate Codec B (EVRC-B)
- QCELP (Qualcomm Code Excited Linear Prediction): QCELP-8 (FFmpeg), QCELP-13 (FFmpeg)
- Selectable Mode Vocoder (SMV)
- Variable Multi Rate – WideBand (VMR-WB)
Professional mobile radio
APCO
- Project 25 Phase 2 Enhanced Full-Rate (AMBE+2 4400bit/s with 2800bit/s FEC)
- Project 25 Phase 2 Half-Rate (AMBE+2 2450bit/s with 1150bit/s FEC) – also used in NXDN and DMR: mbelib
- Project 25 Phase 1 Full Rate (IMBE 7200bit/s): mbelib
European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI)
- ETS 300 395-2 (TETRA ACELP 4.6kbit/s)
TETRAPOL
- RPCELP 6kbit/s
D-STAR Digital Voice (AMBE 2400bit/s with 1200bit/s FEC)
- mbelib
Professional Digital Trunking System Industry Association (PDT Alliance) standards
- NVOC
Spirit DSP RALCWI
DSPINI
- SPR Robust
- TWELP Robust
Codec2
- libcodec2
RL-CELP
Military
U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) Federal Standard
- FS-1015 (a.k.a. LPC-10): HawkVoice (libHVDI)
- FS-1016 (CELP): HawkVoice (libHVDI)
- FS-1023 (CVSD 12kbit/s)
United States Military Standard (MIL-STD)
- MIL-STD-188 113 (CVSD 16kbit/s and 32kbit/s): SoX (libsox)
- MIL-STD-3005 (a.k.a. MELP): Texas Instruments’ 2.4 kbit/s MELP Proposed Federal Standard speech coder
NATO
- STANAG 4198 (a.k.a. LPC-10e)
- STANAG-4591 (a.k.a. MELPe)
BBN NRV
Video games
Bink Audio, Smacker Audio
- FFmpeg
Actimagine (Nintendo European Research & Development) FastAudio
- MobiclipDecoder
- FFmpeg
Nintendo GCADPCM (a.k.a. DSP ADPCM or THP ADPCM)
- vgmstream
- VGAudio
- FFmpeg
Sony VAG (a.k.a. Sony PSX ADPCM)
- vgmstream
- FFmpeg
Sony HEVAG
- vgmstream
Sony ATRAC9
- VGAudio
- FFmpeg
Microsoft XMA
- FFmpeg
Xbox ADPCM
- vgmstream
CRI ADX ADPCM
- vgmstream
- VGAudio
- FFmpeg
CRI HCA/HCA-MX
- vgmstream
- VGAudio
- FFmpeg
- libcgss
- HCADecoder
FMOD FADPCM
- vgmstream
Open-Source Audio Codec Formats List
Among the above numerous audio formats’ codecs, some of them are open-source. They are listed below.
- FLAC
- LAME
- TooLAME/TwoLAME
- Musepack
- Speex
- CELT
- libopus
- libvorbis
- iLBC
- iSAC
- TTA
- WavPack
- Bonk
- Apple Lossless
- Fraunhofer FDK AAC
- FFmpeg codecs in the libavcodec library
- FAAD2
- libgsm
- opencore-amr
- liba52
- libdca
- Codec2
Related Articles



![[Solved] How to Fix “Adobe Media Encoder Is Not Installed”?](https://images.minitool.com/videoconvert.minitool.com/images/uploads/2023/02/adobe-media-encoder-is-not-installed-thumbnail.png)

![[7+1 Ways] How to Fix Adobe Media Encoder Error Code 3?](https://images.minitool.com/videoconvert.minitool.com/images/uploads/2023/03/adobe-media-encoder-error-code-3-thumbnail.png)

![[9 Ways] Fix Adobe Media Encoder Not Connecting to Project](https://images.minitool.com/videoconvert.minitool.com/images/uploads/2023/03/adobe-media-encoder-not-connecting-to-project-thumbnail.png)
![[Solved] How to Fix After Effects Not Sending to Media Encoder?](https://images.minitool.com/videoconvert.minitool.com/images/uploads/2023/04/after-effects-not-sending-to-media-encoder-thumbnail.png)



User Comments :