This article expressed by MiniTool Software mainly elaborates on the meaning/definition, function, types, comparison, as well as editing of video encoder (video codec). After reading this post, you will have a better understanding of how various formats of videos come into being.
To learn video encoder, just get to know what is video codec.
What is a video codec? A video codec is a kind of software or hardware that compress and decompresses digital video. In the context of video compression, “codec” is a portmanteau of encoder and decoder.
What Is A Video Encoder?
A video encoder refers to a device, either software or hardware, that (only) compresses digital videos, whereas a device that (only) decompresses a video is called a video decoder.
Usually, the compressed data format conforms to a standard video coding format. The compression is often lossy. That is to say, the compressed videos lack some information present in the original videos. As a result, decompressed videos have lower quality than the source ones for there is insufficient info to accurately reconstruct the original videos.
There are complicated relationships between the video quality, the amount of data used to represent the video (bitrate), the complexity of the encoding and decoding algorithms, sensitivity to data losses and errors, ease of editing, random access, as well as an end-to-end delay (latency).
The Applications of Video Codecs
Video codecs are applied in DVD players, Internet video, video on demand (VoD), videotelephony, digital cable (HDMI), digital terrestrial television, as well as various other apps. Especially, video codecs are widely used in programs that record or transfer videos, which may not be feasible with the high data volumes and bandwidths of uncompressed video.
Any video file or stream can be encoded with a wide variety of live video formats. Some video encoder H.264 settings need to be set when streaming to an HTML5 video player.
Common Video Codec Format
Many video compression formats can be implemented on personal computers (PCs) and in consumer electronics devices. Thus, multiple codecs are available in the same equipment, reducing the need to select a single major video compression format to achieve interoperability.
Standard video compression formats can be applied to multiple video encoders and decoders from multiple sources. For example, video encoded with a standard MPEG-4 Part 2 codec like Xvid can be decoded by any other standard MPEG-4 Part 2 decoder like DivX Pro Codec or FFmpeg MPEG-4 for they all adopt the same video format.
Codec Packs
Since online video data is encoded by various codecs, codec packs come into being. It is a pre-assembled set of usually used codecs combined with an installer available as a software package for PCs. Some popular codec packs are the K-Lite codec pack and Perian and Combined Community codec pack.
How to Change Video Encoder Format?
If you get a video but your current media player can’t play it for the video codec not supported by the player, you need to convert the video encoder to the supported type of your video player. Thus, you need a video codec converter such as MiniTool Video Converter, a free video and audio format converting program.
MiniTool Video ConverterClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
1. Download, install, and launch MiniTool Video Converter on your Windows computer.
2. By default, you will enter the Converting subtab under the Video Convert tab. There, click the big + icon in the center of the screen to add your video.
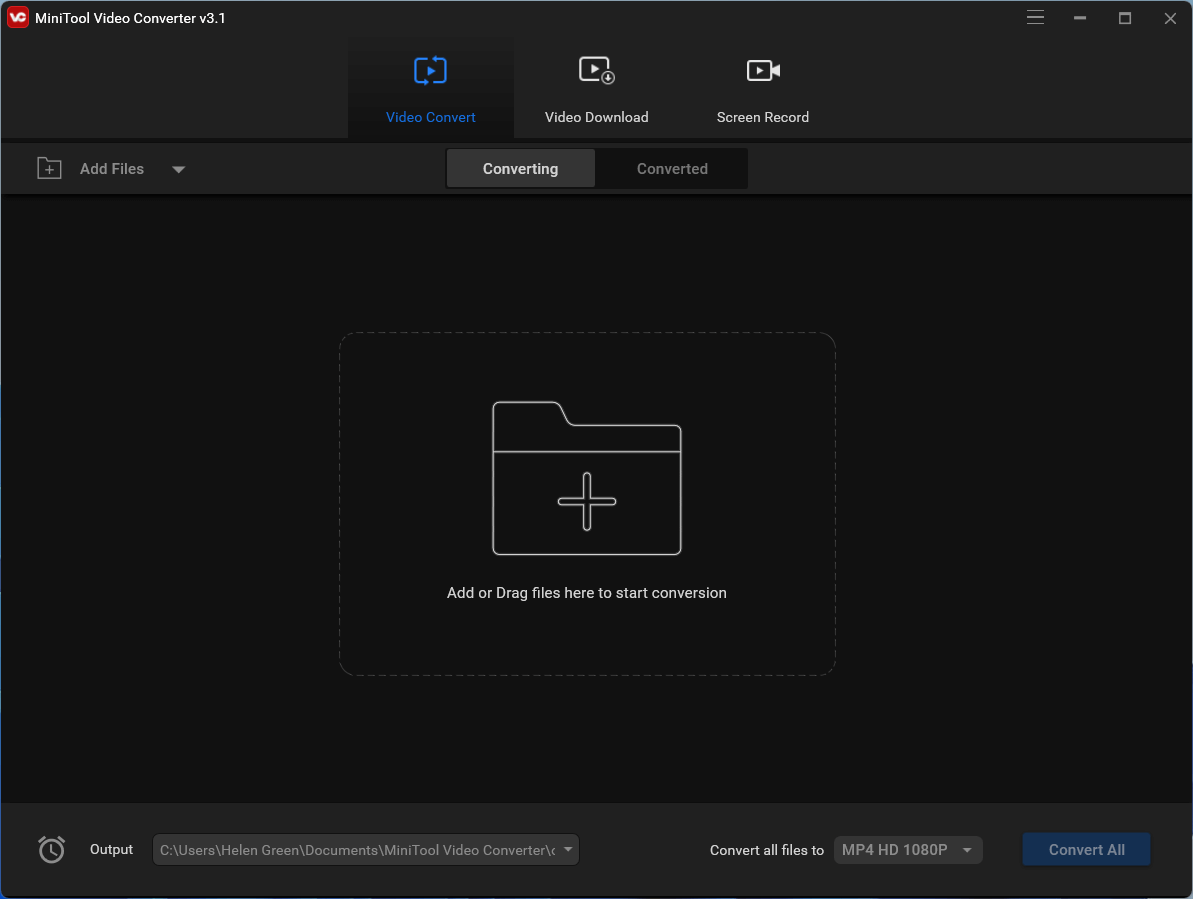
3. Click on the setting icon (an arrow pointing into a square) within the Target section to trigger the output format settings window.
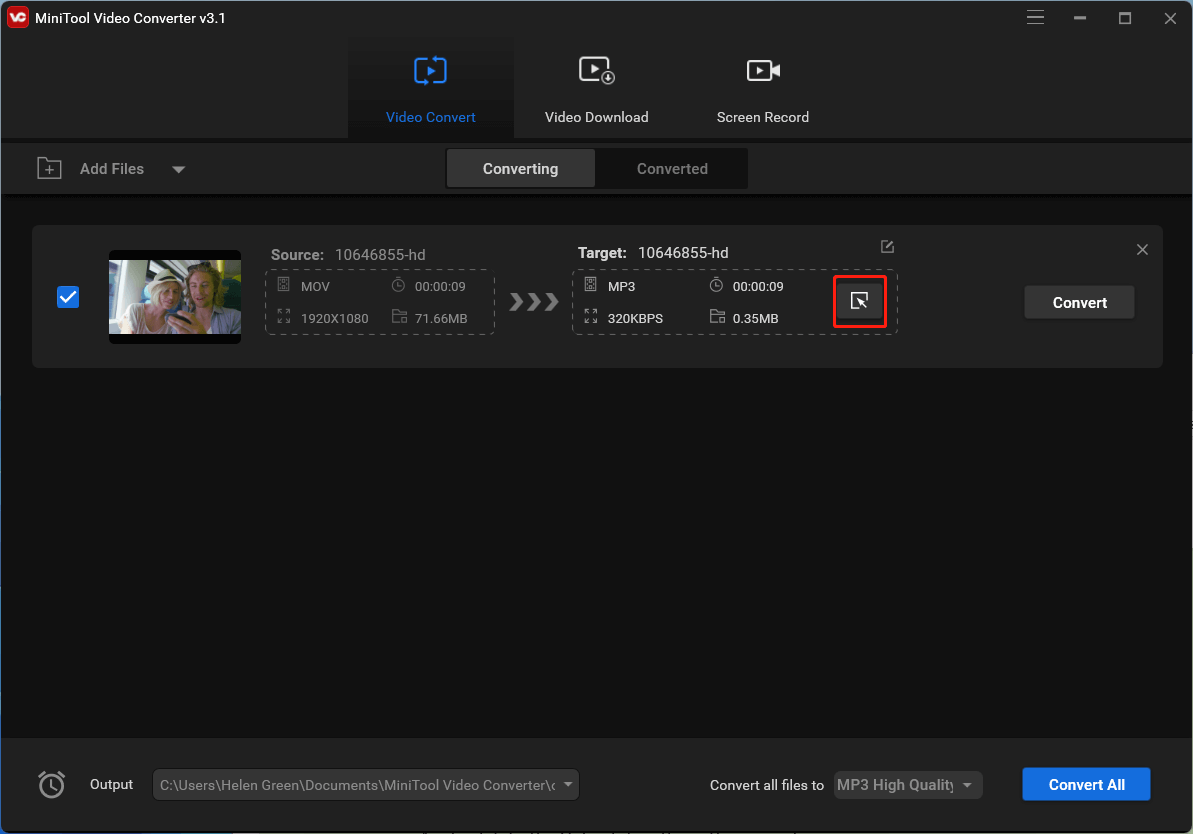
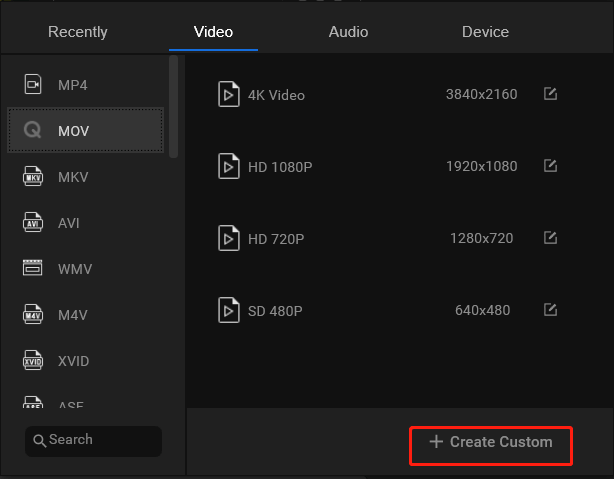
4. Switch to the Video tab in the settings window and select a video format in the left menu. If you don’t want to alter other parameters of your video, just choose the same format and click on the Create Custom option in the bottom right.
5. In the next popup, find the Encoder option under the Video section and pick up a compatible video codec from the drop-down menu.
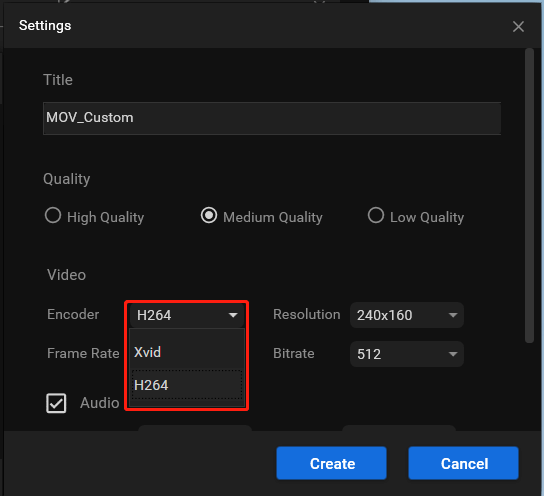
6. click the Create button to create your customized video format and select it when you are redirected back to the video tab.
7. Finally, click the Convert button in the main window to start the process.
Wait until it completes. Then, you can play the video with your media player.
History of Video Encoding
In the past, a video was saved as an analog signal on magnetic tape. When the compact disc (CD) was developed and used as a digital alternative for analog audio, people find it possible to directly store and deliver video in digital form.
To record and convey raw video, you need a large amount of storage space and bandwidth. To improve that situation, engineers and mathematicians have found many ways involving the compression of digital video data.
H.261 was the first practical video coding standard. It was developed by a number of companies including Hitachi, PictureTel, Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT), BT, Toshiba, as well as many others. The most popular video coding standards are the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) standards.
In 1991, MPEG-1 was developed by the group. It was designed to compress Video Home System (VHS) quality video. In 1994, MPEG-1 was succeeded by MPEG-2/H.262. The successor was developed by those companies: Sony, Thomson, Mitsubishi Electric, etc. MPGE-2 became the standard video format for DVD and SD digital television (TV).
In 1999, MPET-4/H.263 came into being, which was a major leap forward for video compression technology. Also, a lot of firms had contributed to the development of MPEG-4 including Mitsubishi Electric, Hitachi, and Panasonic.
However, the most widely used video coding format nowadays is MPET-4 AVC (H.264), which was developed in 2003 by these organizations: Panasonic, Good Kaisha IP Bridge, LG Electronic, and so on. H.264 is the main video encoding standard for Blu-ray Discs. It is also widely accepted by web applications including Adobe Flash Player and Microsoft Silverlight; streaming network services like YouTube, Vimeo, iTunes Store, and Netflix; as well as many high-definition television (HDTV) broadcasts over terrestrial and satellite TV.
In 2013, AVC (Advanced Video Coding) had been succeeded by High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 or MPEG-H Part 2. It is heavily patented by Samsung Electronics, General Electric Company (GE), NTT, and JVC Kenwood. However, the adoption of HEVC has been hampered by its complex licensing structure. In turn, HEVC was succeeded by Versatile Video Coding (VVC).
In addition, there are free VP8, VP9, and AOMedia Video 1 (AV1) video coding formats adopted by YouTube, all of which were developed with involvement from Google.
Since the features and applications of each video coding format are different, there is no best video encoder format for all, but good video encoder formats; or, just the best video encoder format for a certain type of situation.
List of Video Codecs
A video coding format, also called video compression format, is a content representation format for storage or transmission of digital videos such as in a data file or bitstream. Typically, it makes use of a standardized video compression algorithm, most commonly based on discrete cosine transform (DCT) coding and motion compensation.
Video Codec vs. Video Format
A specific hardware or software implementation capable of compression or decompression to/from a specific video coding format is called a video codec. For instance, FFmpeg a the most common video codec for many video formats like H.264, CorePNG, and VP9.
First of all, the video compression formats can be sorted into 3 categories, non-compression, lossless compression, and lossy compression.
# Non-Compression Video Codec Formats
- RGB
- YUV: Intel IYUV
- 10-bit uncompressed video
- Composite digital signal
- Avid DNxUncompressed
- V210
# Lossless Video Codec Formats
ITU-T/ISO/IEC standards
- H.264: x264, FFmpeg
- H.265: x265, UHDcode, FFmpeg
- Motion JPEG 2000: libopenjpeg
- JPEG XS: FastTICO-XS
IETF standards
- FFV1: FFmpeg
SMPTE standards
- VC-2 HQ: libdirac, libschroedinger
Alparysoft Lossless Video Codec (Alpary)
Apple Animation (QuickTime RLE)
- QuickTime
- FFmpeg
ArithYuv
AV1
- libaom
AVIzlib
- LCL (VfW codec) MSZH and ZLIB
- FFmpeg
Autodesk Animator Codec (AASC)
- FFmpeg
CamStudio GZIP/LZO
- FFmpeg
Chennai Codec (EVX-2)
Dxtory
- FFmpeg
FastCodec
Flash Screen Video v1/v2
- FFmpeg
FM Screen Capture Codec
- FFmpeg
Fraps codec (FPS1)
- FFmpeg
Grass Valley Lossless
- Grass Valley Codec Option
- FFmpeg
Huffyuv
- FFmpeg
IgCodec
Intel RLE
innoHeim/Rsupport Screen Capture Codec
- FFmpeg
Lagarith
- Lagarith Codec (VfW codec)
- FFmpeg
LOCO
- FFmpeg
MagicYUV
- MagicYUV SDK
- FFmpeg
Microsoft RLE
MSU Lossless Video Codec
MSU Screen Capture Lossless
CorePNG
- FFmpeg
ScreenPresso (SPV1)
- FFmpeg
ScreenPressor
- FFmpeg
SheerVideo
- FFmpeg
Snow lossless
- FFmpeg
TechSmith Screen Capture Codec (TSCC)
- EnSharpen Video Codec for QuickTime
- FFmpeg
Toponoky
Ut Video Codec Suite
- libutvideo
- FFmpeg
VBLE
- FFmpeg
VMnc VMware screen codec
- FFmpeg
VP9
- libvpx
- FFmpeg
YULS
ZeroCodec
- FFmpeg
ZMBV (Zip Motion Block Video) Codec
- FFmpeg
Lossless game codecs
DXA
- ScummVM Tools
- FFmpeg
# Lossy Video Codec Formats
Discrete cosine transform (DCT)
General
ITU-T/ISO/IEC standards
- H.120
- H.261 (a.k.a. Px64): FFmpeg H.261 (libavcodec), Microsoft H.263
- MPEG-1 Part 2 (MPEG-1 Video): Elecard MPEG-1 video Encoder/Decoder, FFmpeg, MainConcept MPEG-1, TMPGEnc
- H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2 (MPEG-2 Video): Canopus ProCoder, Cinema Craft Encoder, Elecard MPEG-2 Video Decoder/Encoder, FFmpeg, InterVideo Video Decoder, MainConcept MPEG-2, Microsoft H.263, TMPGEnc
- H.263: FFmpeg H.263
- MPEG-4 Part 2 (MPEG-4 Advanced Simple Profile): 3ivx, DivX, Elecard MPEG-4 Decoder/Encoder, libavcodec, HDX4, Nero Digital, Xvid video codec
- H.264/MPEG-4 AVC or MPEG-4 Part 10 (MPEG-4 Advanced Video Coding): CoreAVC, Elecard AVC Decoder/Encoder, MainConcept, Nero Digital, QuickTime H.264, Sorenson AVC Pro, OpenH264, x264, FFmpeg
- MPEG-4 AVC variants: MPEG-4 Web Video Coding or MPEG-4 Part 29, XAVC
- HEVC (High-Efficiency Video Coding, H.265, MPEG-H part 2): x265
- Versatile Video Coding: VVC Test Model, Fraunhofer Versatile Video Decoder, Fraunhofer Versatile Video Encoder
- Video Coding for Browsers (VCB)/VP8 (MPEG-4 Part 31): libvpx, FFmpeg
- Internet Video Coding (MPEG-4 IVC)
- Essential Video Coding (EVC; MPEG-5 Part 1)
- Low Complexity Enhancement Video Coding (LCEVC; MPEG-5 Part 2)
IETF Internet Draft (NETVC)
- xvc
- Thor
SMPTE standards
- VC-1: FFmpeg
- Dirac: Schrödinger, dirac-research, FFmpeg
Alliance for Open Media
- AV1: libaom, SVT-AV1, rav1e, dav1d, libgav1
Xiph.Org Foundation
- Daala
- Theora: FFmpeg, libtheora
Apple Video (Apple RPZA)
- QuickTime
- FFmpeg
Blackbird
Firebird
Digital Video Interactive standards
- RTV 2.1 (a.k.a. Indeo 2): FFmpeg
- PLV (Production Level Video)
Indeo 3/4/5
Microsoft Video 1 (MSV1, MS-CRAM)
Open Media Commons standards:
- OMS Video
On2 Technologies
- FFmpeg
RealVideo 1, G2, 8, 9 and 10
- FFmpeg
- RealMedia HD SDK
RealVideo Fractal Codec (a.k.a. Iterated Systems ClearVideo)
- FFmpeg
RealMedia HD (a.k.a. RealVideo 11)
- RealMedia HD SDK
Snow Wavelet Codec
Sorenson Video, Sorenson Spark
- FFmpeg
VP9
- libvpx
- FFmpeg
Windows Media Video (WMV)
- WAX
- FFmpeg
Guobiao standards (GB/T)
- Audio Video Standard (AVS): AVS1-P2 (FFmpeg), AVS1-P7 (AVS-M), AVS2-P2 (uAVS2/xavs2/davs2), AVS3-P2 (uavs3e/uavs3d)
Scalable
VP8, VP9, AV1, and H.266/VVC support scalable modes by default.
- Scalable Video Coding (H.264/SVC)
- Scalable High-Efficiency Video Coding (SHVC)
Intra-frame-only
Motion JPEG
- FFmpeg
- Morgan Multimedia M-JPEG
- Pegasus PICVideo M-JPEG
- MainConcept M-JPEG
ISO/IEC standard
- Motion JPEG 2000: libopenjpeg, FFmpeg, Morgan Multimedia M-JPEG2000, Morgan Multimedia dcpPlayer
- JPEG XS: intoPIX fastTICO-XS
- DV: FFmpeg
- MPEG-4 SStP: FFmpeg
- Motion JPEG XR
Apple ProRes 422/4444
- FFmpeg
Apple Intermediate Codec
- FFmpeg
Apple Pixlet
- FFmpeg
AVC-Intra
- x264
- FFmpeg
AVC-Ultra
XAVC-I
CineForm HD
- CineForm-SDK
- FFmpeg
SMPTE standard
- VC-2 SMPTE (a.k.a. Dirac Pro.): Schrödinger, dirac-research, VC-2 Reference video Encoder and Decoder, FFmpeg
- VC-3 SMPTE: Avid DNxHD, FFmpeg
- VC-5 SMPTE
Grass Valley HQ/HQA/HQX
- Grass Valley Codec Option
- FFmpeg
NewTek NT25
NewTek SpeedHQ
- FFmpeg
Stereoscopic 3D
Multiview Video Coding
Security and surveillance cameras
Guobiao standards
- AVS-S-P2
- SVAC
Infinity CCTV Codec (IMM4/IMM5/IMM6)
- FFmpeg
CD-ROM or CD-related video codecs
- CDXL codec: FFmpeg
- Cinepak (a.k.a. Apple Compact Video): FFmpeg
- Photo CD codec: FFmpeg
- MotionPixels: FFmpeg
- CD+G (CD+Graphics): FFmpeg, VLC
- CD+EG (CD+Extended Graphics)
Network video codecs
- HEVC-SCC
- ZRLE
- Sun Microsystems’ CellB video (RTP playload type 25)
- Xerox PARC’s Network Video (nv; RTP playload type 28)
- CU-SeeMe
- GoToMeeting: FFmpeg
Bayer video codecs
- CinemaDNG
- Redcode RAW: libredcode
- ArriRaw
- Cineform RAW: CineForm-SDK
- Blackmagic RAW: Blackmagic RAW SDK
- Cintel RAW: FFmpeg
- Apple ProRes RAW
- intoPIX TICO RAW: intoPIX fastTICO-RAW SDK & TICO-RAW FPGA/ASIC libraries
Video games
- Bink Video/Smacker video: FFmpeg, libavcodec
- Nintendo Mobiclip: FFmpeg
- CRI Sofdec
- CRI P256
- Indeo Video Interactive (aka Indeo 4/5): FFmpeg, Intel Indeo Video
Real-time
- Hap/Hap Alpha/Hap Q: VIDVOX hap codec, FFmpeg
- DXV Codec: Resolume DXV Codec, FFmpeg
- NotchLC: FFmpeg
- VESA Display Stream Compression (DSC)
- VESA Display Compression-M (VDC-M)
List of Open-Source Video Codecs
Among the above video codecs list, some of the codecs are open-source.
- x264
- OpenH264
- x265
- Xvid
- libvpx
- SVT-AV1
- VideoLAN dav1d
- Org rav1e
- Google libgav1
- xvc
- FFmpeg
- Lagarith
- libtheora
- Dirac as dirac-research
- Huffyuv
- Daala
- Thor
- Turing
- libaom
- Kvazaar
- VVenC & VVdeC
Comparison of Video Codecs
The primary goal of most video compression solutions is to produce videos that most closely approximate the fidelity of the original videos while delivering the smallest file size. Besides some other factors that need to consider when comparing the codecs of videos include video quality per bitrate (range of bitrate), performance, and general software characteristics.
# Video Quality
Objective video quality
- Full reference
- Reduced reference
- No-reference
Subjective video quality
- Pre- and post-filters
- Motion estimation (ME) search strategy
- Rate control strategy
# Performance
Seed comparison
- Decompression frame time uniformity
- SIMD support
- Multi-threading support
- RAM speed
- Processor cache size
- GPU usage
Profiles support
- Baseline profile (BP)
- Main profile (MP)
- Extended profile (XP)
- High profile (HiP)
- High 10 profile (Hi10P)
- High 4:2:2 profile (Hi422P)
- High 4:4:4 predictive profile (Hi444PP)
- Multiview high profile
- High 10 intra profile
- High 4:2:2 intra profile
- High 4:4:4 intra profile
- CAVLC 4:4:4 intra profile
- Scalable baseline profile
- Scalable high profile
- Scalable high intra profile
Supported rate control strategies
- Variable bitrate (VBR)
- Constant bitrate (CBR)
# Software Characteristics
- supported OS: Windows, Linux (e.g. Ubuntu), macOS
- technical details: compression type, basic algorithm, highest supported bitrate/resolution, variable frame rate.
- supported interfaces: VfW, DirectShow, etc.
- price: value for money, volume discounts, etc.
- license type: free, open-source, commercial
- manufacturer,
- version number
- release date
Related Articles




![[Solved] How to Fix After Effects Not Sending to Media Encoder?](https://images.minitool.com/videoconvert.minitool.com/images/uploads/2023/04/after-effects-not-sending-to-media-encoder-thumbnail.png)
![[9 Ways] Fix Adobe Media Encoder Not Connecting to Project](https://images.minitool.com/videoconvert.minitool.com/images/uploads/2023/03/adobe-media-encoder-not-connecting-to-project-thumbnail.png)

![[7+1 Ways] How to Fix Adobe Media Encoder Error Code 3?](https://images.minitool.com/videoconvert.minitool.com/images/uploads/2023/03/adobe-media-encoder-error-code-3-thumbnail.png)

User Comments :