This article provides a comprehensive analysis of automatic speech recognition (ASR), covering its definition, working principle, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. Additionally, it recommends three reliable ASR software options: MiniTool Video Converter, Google Docs Voice Typing, and Otter.ai.
What Is Automatic Speech Recognition
You may have seen the abbreviation ASR in many articles. What is ASR? I will explain to you what it is, its history, main systems, and characteristics below.
Automatic Speech Recognition Meaning
The following is an explanation of automatic speech recognition and how it differs from Speech-to-Text (STT).
What Is ASR
Automatic speech recognition is an artificial intelligence technology that converts speech to text. This technology is now widely used in various fields. Many entrepreneurs and professionals have begun using automatic speech recognition as a productivity tool.
Automatic speech recognition can easily convert audio signals into written text. Furthermore, this technology can understand languages from different countries or regions, even multiple dialects and accents. Its versatility makes it indispensable for real-time captioning, instant meeting transcripts, and hands-free clinical documentation.
ASR vs. STT
When discussing speech-based artificial intelligence, we often encounter the terms Automatic Speech Recognition and Speech-to-Text. Both refer to converting spoken language into written text. However, the final texts they generate are quite different.
ASR typically converts the raw audio directly into text without punctuation or capitalization. This is because automatic speech recognition needs to ensure the speed and accuracy of subsequent machine processing. However, this also means that this text format is not suitable for human reading.
STT, on the other hand, converts audio to text with punctuation, capitalization, and speaker labels. This text format is easy for humans to read, search, and archive. Because speech-to-text technology generates text that includes punctuation marks, it can accurately record the speaker’s original meaning. Therefore, this technology is often used for court transcripts.
History of Automatic Speech Recognition
Automatic speech recognition has undergone years of development. It began with systems that could only recognize single numbers and is now smart enough to understand normal speech. Here are the main steps in its journey. The following are the key stages in the development of ASR technology:
1. 1950s to 1970s:
Automatic speech recognition systems can be traced back to 1952 with the Audrey program, which was developed by Bell Labs. This program could transcribe simple numbers from one to nine.
Subsequently, IBM introduced the “Shoebox,” a speech recognition system that could understand and distinguish 16 English words, including the numbers 0 to 9, as well as the words plus, minus, total, subtotal, false, and off. In 1976, Carnegie Mellon University developed the “Harpy” system, which could recognize more than 1,000 words.
2. 1970s to 2010s:
Researchers successfully transcribed some words using the Hidden Markov Model (HMM). This model extracts the smallest sound units (phonemes) from audio and uses the HMM to analyze and guess the correct words based on commonly used ones. Furthermore, the model can find the best-matching word through context. Today’s ASR technology is based on and improved from the HMM model.
3. 2010s to Present:
In the 2010s, deep learning technology was applied to speech recognition. This move improved the accuracy of speech recognition to unprecedented levels. Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant, and Amazon Alexa are now widely used on various devices.
Automatic Speech Recognition Types
Automatic speech recognition can be categorized into six types based on the system, function, and dependence on the speaker. The following is a detailed explanation of these types.
#1 Classified by System Design
There are two primary ASR systems: the hybrid model and the end-to-end model. Therefore, ASR can be categorized as either hybrid or end-to-end.
1. Hybrid ASR
The hybrid model is the first-generation model used by ASR. It combines multiple different models in a specific arrangement. Executing these models sequentially converts audio to text. The following is the order and function of these models:
- Turn the sound into a simple picture that shows its pitches and loudness.
- Use the neural network to predict relevant phonemes based on context every 10 milliseconds.
- Remove adjacent sounds and only keep the fundamental sounds.
- Use a dictionary model to convert the phoneme sequence into a word sequence.
- Use a fully trained language model to select truly meaningful word sequences from the identified word sequences.
2. End-to-End ASR
End-to-end speech recognition models are much simpler than hybrid models. This model does not use complex multi-component processes, but instead replaces them with a single large neural network. This makes the system simpler, more efficient, and generally more accurate.
#2 Classified by Function
Based on the function, speech recognition can be divided into grammar ASR and transcription ASR. Below is a simple and easy-to-understand explanation of them.
1. Grammar ASR
Grammar ASR relies on a complete and closed set of grammar rules. These rules predefine vocabulary and their corresponding instructions. It’s important to note that these instructions are limited. When you give a command, the ASR engine will target specific words or sentences.
To put it simply, grammar ASR cannot understand complete conversations. It can only understand specific intentions. The airport parking hotline is a good example. When you ring the line, it says: “Say 1 for Terminal A, 2 for Terminal B, 3 for economy.” You just need to tell the corresponding number, and it will instantly know where you want to park.
Grammar ASR has clear grammatical rules and a limited vocabulary, which greatly reduces the possibility of misunderstanding. Therefore, it has a very high accuracy rate. Nowadays, grammar ASR is widely used in interactive voice response (IVR) systems.
2. Transcription ASR
Transcription ASR can recognize every word you speak, as well as accent and tone. Therefore, achieving high accuracy in transcription ASR requires a model that can cover all languages and dialects of all countries and regions. This is extremely challenging.
For example, Zoom’s live captioning feature for meetings uses transcription ASR. You can also download the transcript of a Zoom recording. Because this transcript completely records all the content of the meeting and the speakers, you can quickly search for important information. Furthermore, the transcript can be translated into other languages to increase accessibility.
There is no inherent advantage or disadvantage between grammar ASR and transcription ASR. The choice between these two speech recognition methods depends on your needs. If you want to predict user responses within a limited scope, grammar ASR is more suitable. On the other hand, if you need to transcribe conversations, podcasts, meetings, or other audio verbatim, then transcription ASR is the ideal choice.
#3 Classified by Speaker Dependency
Based on whether speech recognition depends on a specific speaker, it can be divided into speaker-dependent ASR and speaker-independent ASR.
1. Speaker-Dependent ASR
Speaker-dependent ASR can recognize the voice of a specific individual. This type of speech recognition is built by training the system with the voice of a particular person. After extensive training, the system can recognize a large number of commands with very high accuracy. However, a speaker-dependent system can only accurately recognize the voice of the person it was trained on. It cannot understand the voices of other people.
2. Speaker-Independent ASR
Speaker-independent ASR system is developed using extensive datasets that include a wide variety of voices, accents, and speaking styles from numerous speakers. Therefore, it can recognize specific words regardless of the speaker. This system also provides a high level of accuracy, though it is slightly less accurate than speaker-dependent ASR.
Key Features of Effective ASR
Currently, you can find a wide variety of speech recognition applications and devices on the market. What are the characteristics of effective automatic speech recognition? Here are some aspects you can refer to.
- Speaker Recognition: The system can quickly identify different speakers in audio. During the generated transcript, each speaker is labeled, and their remarks are categorized under the corresponding speakers.
- Acoustic Adaptation: The system can adapt to different acoustic environments. It automatically “listens to the room,” checking the quality of the microphone, as well as the echo, speaker pitch, volume, and speaking speed. These adjustments make speech recognition more accurate.
- Industry Terminology Database: The system includes terminology databases from various industries, such as medicine and law. It can also recognize some product names.
- …
The above has introduced the definition, history, types, and features of automatic speech recognition. How exactly does it convert speech to text? Let’s find out in the next section.
How Does Automatic Speech Recognition Work
The emergence of speech recognition technology has brought us many conveniences. How does it convert audio to text? This brings us to the two main methods used in ASR: the traditional hybrid approach and the end-to-end deep learning approach.
Traditional Hybrid Approach
The traditional hybrid method has dominated the history of speech recognition development and is still in use today. This method comprises multiple independent models, including acoustic models (Hidden Markov Models and Gaussian Mixture Models), dictionary models, and language models.
By processing the above three models sequentially, the text transcription can eventually be generated. In essence, this method searches through every possible solution to pinpoint the most accurate one.
End-to-end Deep Learning Approach
The end-to-end deep learning method uses a single neural network to complete the entire speech recognition process. This is a common approach in modern speech recognition technology. It is more accurate and efficient than traditional hybrid methods. The workflow of an end-to-end deep learning system consists of two steps. First, use the encoder to convert the raw audio into a smart summary, and then use the decoder to output the actual words.
Workflow of Automatic Speech Recognition
How exactly does automatic speech recognition convert audio to text? Let’s break down the workflow into five main steps, including acquiring audio, converting the signal, extracting features, matching words, and decoding.
- Acquire Audio Signals: Record the speaker’s voice with a microphone and capture the sound waves.
- Convert Audio Signal to Digital Signal: Reduce the background noise to make the sound clearer, and then convert the audio into a digital signal.
- Extract Features: Identify phonemes in the audio.
- Match Words: Acoustic models associate tiny sound units with possible words, and language models combine these words into fluent, coherent sentences.
- Decode and Output: The decoder selects the most likely word sequence and then adds punctuation, capitalization, and speaker tags.
Now that we understand how automatic speech recognition converts audio to text. Now it’s time to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of this technology.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ASR
Automatic speech recognition is a powerful technology that has significantly improved our daily lives. However, it also has certain limitations.
Advantages of ASR
Now, let’s explore the advantages of automatic speech recognition in detail.
1. Enhanced Accessibility
Automatic speech recognition is extremely helpful for individuals who are visually impaired. Through this technology, they can operate mobile phones, computers, smart home devices, and more using voice commands. Furthermore, ASR can generate live captions for videos, online meetings (such as Zoom and Skype), and lectures, enabling hearing-impaired individuals to access audio content.
2. Higher Accuracy
With technological advancements, some speech recognition software and tools on the market have achieved high accuracy. In particular, models trained using deep learning and massive amounts of data have reached commercially viable levels of accuracy.
Current ASR technology uses neural networks to significantly improve speech feature extraction capabilities. Furthermore, end-to-end models simplify the transcription process and reduce error rates. Additionally, language models enable ASR systems to understand context, resulting in more accurate final outputs.
3. Hands-Free Operation
Currently, automatic voice recognition technology is being applied to various electronic devices. Thanks to this technology, users can control devices and applications entirely through voice commands without lifting a finger.
For example, some car intelligent in-vehicle voice systems allow users to perform various operations, such as communication, playing music, and navigation, without touching the screen or buttons. This ensures that we keep our hands on the steering wheel while driving, greatly improving the safety.
4. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Automatic speech recognition systems can quickly transcribe audio content, greatly simplifying workflows and improving personal and work efficiency. In situations such as meetings, interviews, and lectures, ASR technology can convert spoken words into text. Typically, ASR tools can generate a transcript of audio in minutes or even seconds, while manual transcription takes much longer.
5. Multilingual Support
Automatic speech recognition systems support multiple languages and dialects. They generally support dozens of mainstream languages, including English, French, Spanish, Russian, Japanese, Korean, and more. This allows people speaking different languages to enjoy the convenience of audio transcription.
6. Cost Reduction
Automatic speech recognition systems have helped many companies spend less on wages, because they no longer have to pay people to listen to recordings and type out every word. In the past, businesses often hired human transcribers who charged for each minute of audio. In the United States, the usual fee ranged from $1.50 to $4.00 per minute. If the audio quality is poor, contains background noise, or has a heavy accent, the work will be more difficult, and the price will be higher.
ASR technology has significantly reduced the cost of speech-to-text conversion. Currently, AI transcription tools typically cost $0.10 to $0.30 per minute. Furthermore, some cloud-based ASR services have low hardware or infrastructure requirements, which can help businesses further reduce transcription costs.
7. Real-time Capabilities
Automatic speech recognition systems can not only convert speech to text, but also complete the conversion word by word in real time as the speaker speaks. For example, in online classes, the lecturer’s words can be converted into captions that scroll under the video in real time. This allows students to understand the lecturer even in noisy environments and ensures they do not miss any key points.
8. 24 Hour Uninterrupted Operation
Automatic speech recognition engines never sleep, so you can upload audio and get a transcript at any time. It never gets tired. Even if you give it an audio file in the early hours of the morning, it can still transcribe it into accurate text with high quality.
Disadvantages of ASR
While automatic speech recognition offers great convenience, it also has some shortcomings and limitations. Below are some of the most obvious drawbacks.
1. Easily Affected by Background Noise
Automatic speech recognition model struggles to cope with background noise. This is because noise in the audio can mask the speaker’s voice characteristics, such as pitch and phonemes. This makes it difficult for ASR systems to distinguish between noise and human speech. When the frequency ranges of human speech and noise overlap, the system can easily misidentify words.
Furthermore, ASR systems are typically trained on clean and clear audio, lacking training data with various types of noise. This results in the system being unable to distinguish between noise and signal. Various environmental sounds in daily life can affect automatic speech recognition. For example, conversations between colleagues in an office, keyboard typing sounds, the hustle and bustle of crowds in a busy city, and the roar of cars.
2. Struggles with Poor Audio Quality
Automatic speech recognition has high requirements for audio quality. Low audio quality will result in lower accuracy of audio transcription. Many factors can lead to low audio quality, including audio compression and static interference. For example, during network communication, audio can be excessively compressed, leading to the loss of crucial details. This reduces the quality of the signal received by the ASR system.
3. Inaccurate Recognition at Low Volumes
The performance of automatic speech recognition systems degrades under low-volume conditions. This is mainly because the training data usually consists of clear speech at normal volume, leading to the model being unprepared for lower-volume input. If the volume is low, the speech signal received by the ASR system will be weak, leading to the loss of some crucial details in the audio, ultimately resulting in low accuracy of audio transcription.
4. Difficult to Handle Speaker Variability
Even with excellent audio quality, automatic speech recognition systems also struggle to handle variations in speech between different speakers. Most ASR systems collect data from native speakers. If you are not a native speaker and your pronunciation is not standard, the system may not be able to recognize your speech accurately. Additionally, some ASR systems are difficult to handle various accents and dialects. Speaking too quickly can also negatively impact audio recognition.
5. Struggles with Jargon
Every industry, including medicine, law, and technology, has its own unique terminology. The number of specialized terms in each field is vast and constantly changing. These terms are typically not present in general training data. Therefore, automatic speech recognition models are unable to accurately recognize them.
Automatic speech recognition may not accurately recognize unclear speech, speech with accents, or speech containing too much technical jargon.
Nevertheless, the advantages of ASR generally outweigh the disadvantages, which is why it is widely used in various industries. Below, we will explore how ASR is used in our daily lives.
Automatic Speech Recognition Examples
Automatic speech recognition is ubiquitous in our daily lives. Below are some use cases for this technology.
1. Virtual Voice Assistant
When it comes to automatic speech recognition, the most common examples are virtual voice assistants. They can interact with various smart home devices and online services. Common voice assistants include Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
- Apple Siri: This classic ASR application supports 21 languages and enables hands-free control of calls, messages, weather, calendar, music, and smart home devices.
- Google Assistant: This AI-powered voice assistant can help you complete various tasks, including answering questions, setting alarms, controlling smart home devices, and getting directions.
- Amazon Alexa: This voice control assistant works with Amazon Echo speakers, Fire TV, and many third-party smart devices. It can play music, control smart home devices, create to-do lists, listen to audiobooks, and more.
2. Conference and Meeting
Speech recognition technology is used in many online meetings and webinars. For example, video conferencing tools such as Microsoft Teams and Zoom can generate real-time subtitles and meeting transcripts. ASR technology can also be applied to machine translation. In meetings with participants from different language backgrounds, it can provide real-time translated subtitles for attendees.
3. Medical and Healthcare
Automatic speech recognition is also used in medical recording and controlling medical devices. ASR can record conversations between doctors and patients, generating electronic health records. Additionally, during surgery, surgeons can use ASR technology to control medical devices hands-free. All of these features help doctors save time and improve efficiency.
4. Language Learning
Automatic speech recognition is ideal for learning a language. Software such as Rosetta Stone, Babbel, Duolingo, and Mondly all utilize ASR technology. As the learner speaks, ASR analyzes their pronunciation. If a word is pronounced incorrectly, the system will highlight it and correct the pronunciation, thereby improving the learner’s accent.
5. Media and Broadcasting
Many video-sharing platforms, such as YouTube and Vimeo, support real-time subtitles. This provides accessibility for some hearing-impaired people. In addition, ASR technology can also generate real-time captions for some live TV, sports events, and news content.
6. Legal and Law Enforcement
Automatic speech recognition can be used in the legal field. For example, it can be used to transcribe court testimony in real time or after the fact, generating court transcripts. This is faster and more convenient than manual transcription. What’s more, in law enforcement, it can help police convert oral testimonies and witness statements into written records.
7. Automotive and Transportation
Many cars also integrate ASR systems into their intelligent in-vehicle infotainment systems. Allows drivers to operate the infotainment system without taking their hands off the steering wheel. For example, drivers can control various functions, such as music playback, navigation, and air conditioning, via voice commands, thereby improving safety and convenience.
As the applications demonstrate above, automatic speech recognition plays a vital role in our lives. If you’d like to know which software can address your everyday transcription needs, continue reading the next section.
Top-Rated Automatic Speech Recognition Tools
Automatic speech recognition has become an integral part of our lives. Currently, there are many ASR software on the market. Choosing one that meets your needs is crucial. Next, I will tell you how to evaluate the quality of an ASR tool and provide three of the best ones.
How to Choose the Right Automatic Speech Recognition Software
If you are choosing a speech-to-text tool, please consider the following five points.
1. Accuracy
When audio quality is good and there is no noise, the more diverse the data used to train an automatic speech recognition model, the higher the transcription accuracy. Excellent ASR tools use advanced models that can better predict word order through natural language processing (NLP). These models can then select the correct words based on context.
2. Timestamp
The speech recognition tools you choose should support exporting timestamped text. Timestamps are used to identify the time corresponding to a specific word in the audio or video, facilitating easy navigation within the transcribed text. Common text formats that support timestamps include SRT (SubRip Subtitle), WebVTT (Web Video Text Tracks), TTML (Timed Text Markup Language), SCC (Scenarist Closed Caption), and more.
3. Language Model
Excellent automatic speech recognition software should possess a powerful language model. This model should support multiple languages, be able to learn new words autonomously, and ideally allow users to add specialized vocabulary to improve the accuracy of audio transcription in different fields.
4. Security and Privacy
If the audio you want to transcribe contains private information, choosing software that protects the audio content is crucial.
Generally, offline speech recognition software processes data locally on the device, offering better privacy and security. Online tools, on the other hand, process speech data in the cloud, which may potentially leak user privacy. Therefore, it’s especially important to ensure that online ASR tools comply with data protection laws, such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
5. Offline or Online
Besides privacy mentioned above, the difference between offline and online ASR tools also lies in their network requirements. Offline software can smoothly convert audio to text without an internet connection, making it ideal for use in environments with unstable network connections. On the other hand, when the network signal is weak, online tools may transcribe slowly or fail to transcribe successfully.
Next, I will recommend one offline and two online speech recognition tools. They stand out due to their high accuracy and advanced artificial intelligence features.
Best Offline Automatic Speech Recognition Software
First, I’d like to recommend a highly secure and accurate speech to text software: MiniTool Video Converter. It’s a desktop application.
MiniTool Video Converter’s Intelligent Subtitle feature utilizes an automatic speech recognition system, allowing you to convert video or audio into text in minutes! It supports importing various audio and video formats, including MP3, WAV, AIFF, WMA, M4A, MP4, MKV, MOV, WebM, WMV, etc. Furthermore, this software has no file size limit.
MiniTool Video Converter offers three AI models. Each is suitable for different scenarios:
- Basic Model: Offers standard accuracy and ultra-fast speed. Suitable for routine tasks such as transcribing daily notes.
- Standard Model: Offers higher accuracy and faster speed. Recommended for tasks such as work and study.
- Advanced Model: Offers the highest accuracy and standard speed. Suitable for professional tasks such as video editing.
What’s more, MiniTool Video Converter offers a variety of export options. It allows you to save video/audio transcripts as SRT or TXT files. You can export a video with embedded subtitles.
How to use MiniTool Video Converter to convert video/audio to text? Here is a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Install MiniTool Video Converter on Your PC
To download and install MiniTool Video Converter, click the download button below, then launch the application on your computer.
MiniTool Video ConverterClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
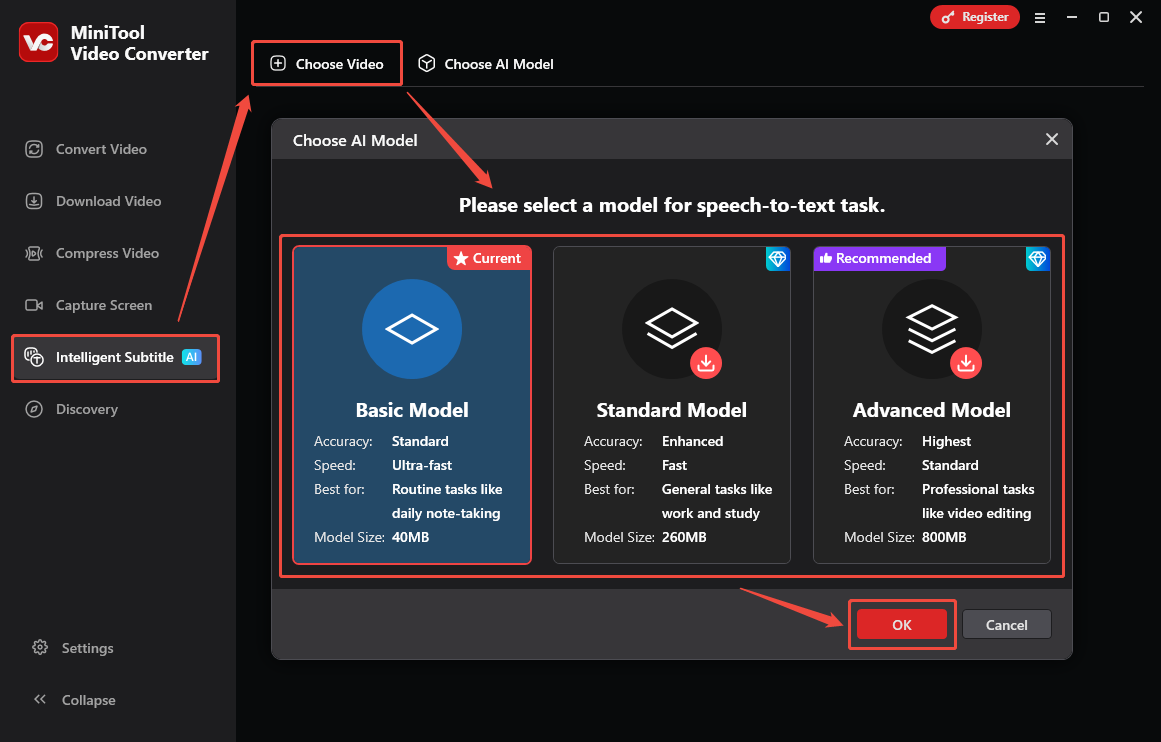
Step 2: Choose an AI Model
Go to the Intelligent Subtitle tab and click on the Choose Video option. Then, the Choose AI Model window will pop up. Choose the AI model you want and click OK to download it.
Step 3: Import Your Audio File
After the AI model finishes downloading, the Import Media window will appear. Then, select your audio file and click OK, and the transcription will begin automatically.
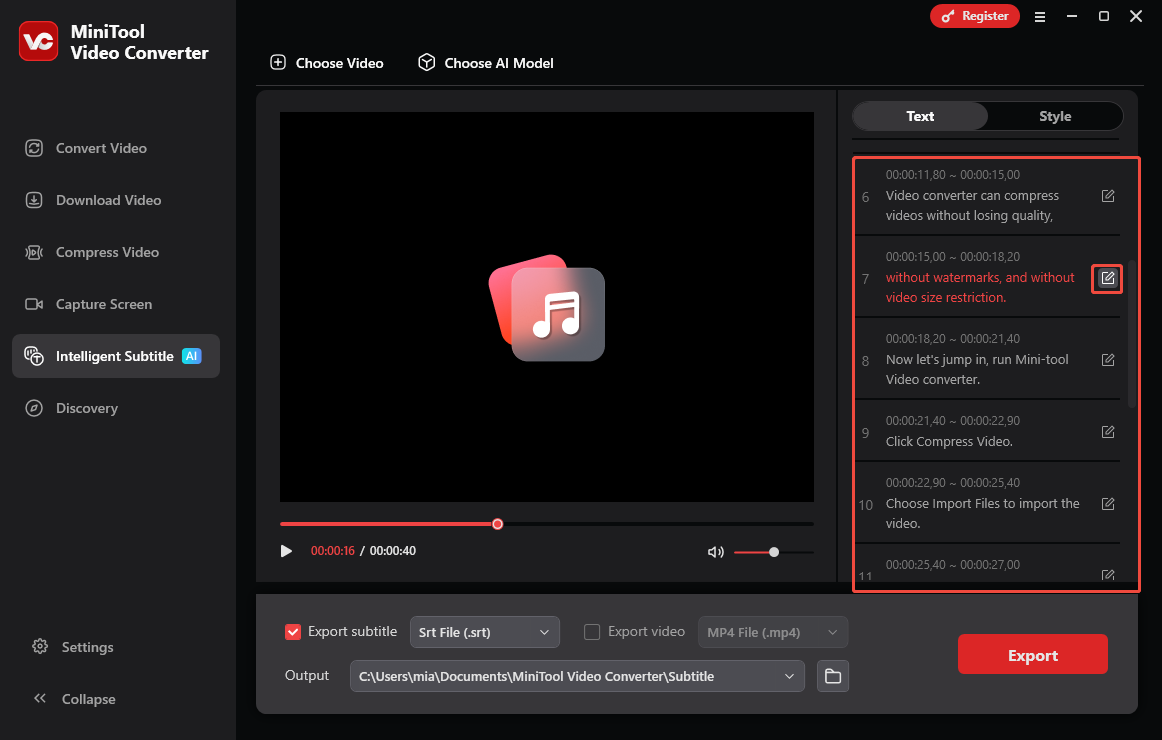
Step 4: Edit the Text If Necessary
Once the transcription is complete, the text will appear in the right-hand panel. You can simply click the edit icon next to any sentence to make changes.
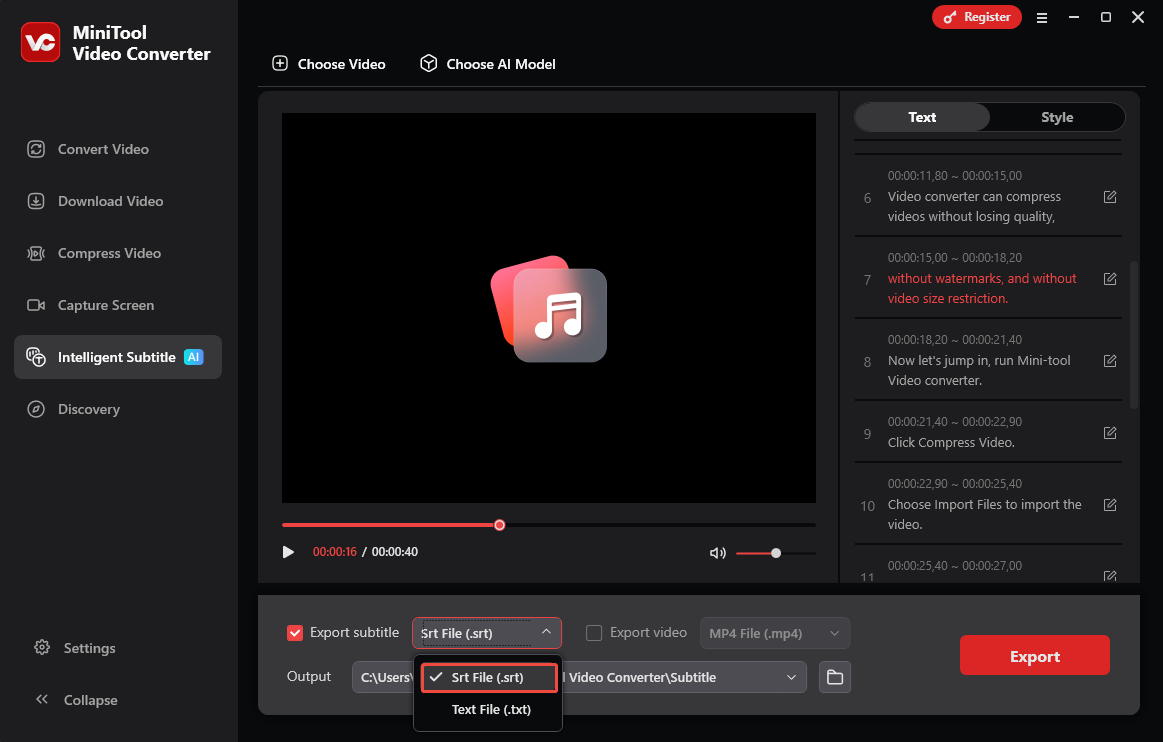
Step 5: Set the Output Format
Open the Export subtitle drop-down, choose SRT or TXT as output format.
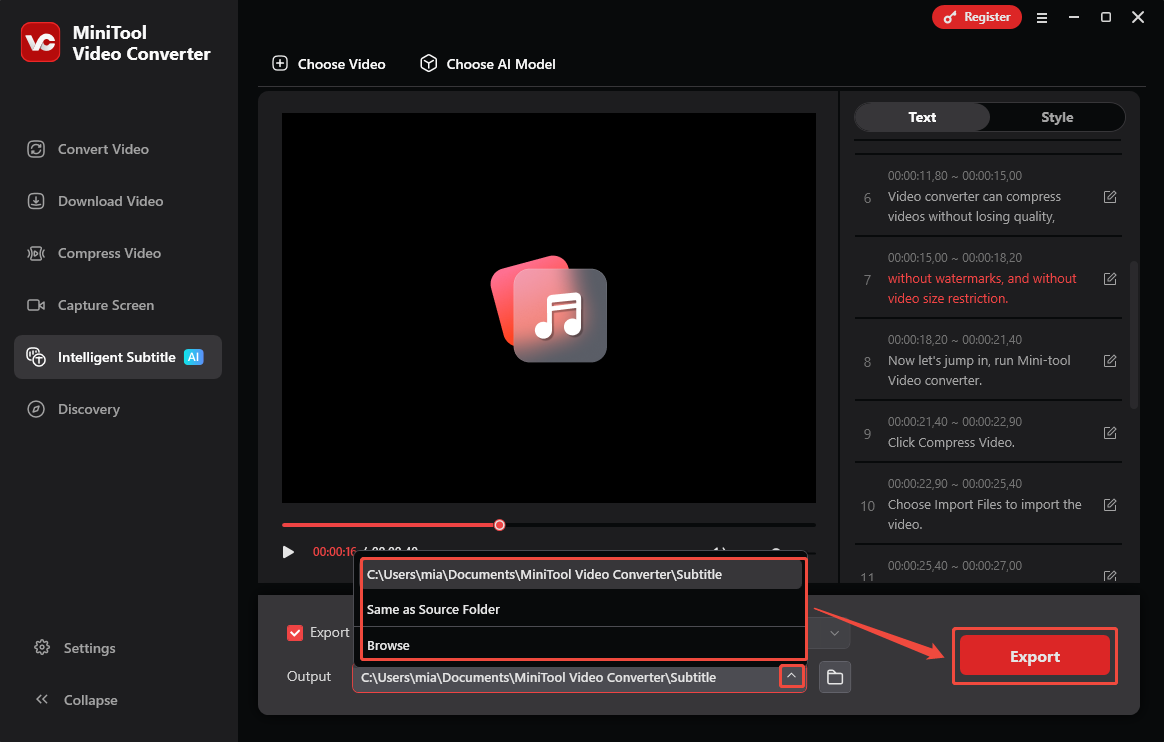
Step 6: Choose the Output Folder
Expand the Output option at the bottom to choose where the text file will be saved.
Step 7: Export the Text File
Click on the Export button in the lower-right corner. When it’s done, the folder pops up so you can check the new text file right away.
Following the steps above, you can use MiniTool Video Converter to convert videos or audio files of any size into text. In addition to this, this software also supports video compression, audio/video format conversion, and adjusting various parameters that affect file size, such as resolution, frame rate, and bitrate. If you’d like to convert speech to text online, please see the next section for two excellent tools.
Best Online Automatic Speech Recognition Tool
Here are two tools that can convert audio to text without installing any software.
1. Google Docs Voice Typing
Google Docs Voice Typing converts speech to text in real time. It offers powerful hands-free functionality for creating and editing documents. This feature is available directly through a web browser or mobile app.
Google Docs Voice Typing supports multiple languages, including English, French, Japanese, German, Spanish, and Korean. It also highlights potential spelling errors and provides intelligent spelling assistance while converting speech to text. It’s ideal for recording discussions and meetings.
Step 1: Create a New Document on Google Docs
Go to https://docs.google.com/ and sign in with your Google account. Then click Blank document to create a new document.
Step 2: Enable Voice Typing
Click on the Tools tab at the top of the document and choose Voice typing from the dropdown.
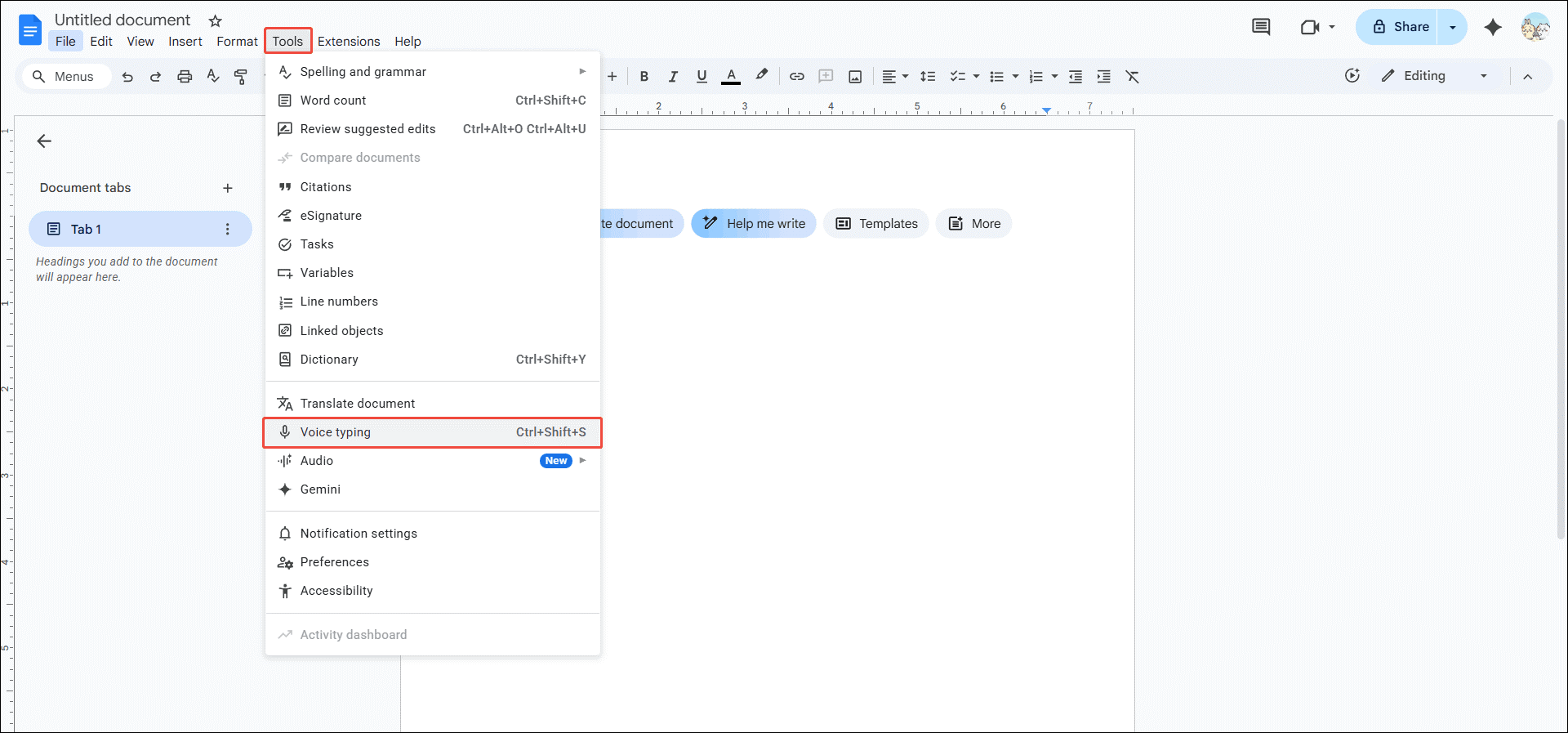
Step 3: Select the Language You Want to Speak
You will see a floating window with a microphone icon. Press the more icon to drag it to any position. Google Docs defaults to English as the recognition language. Click the English (US) option to select other languages.
Step 4: Start Transcribing
Click the microphone icon to start transcribing.
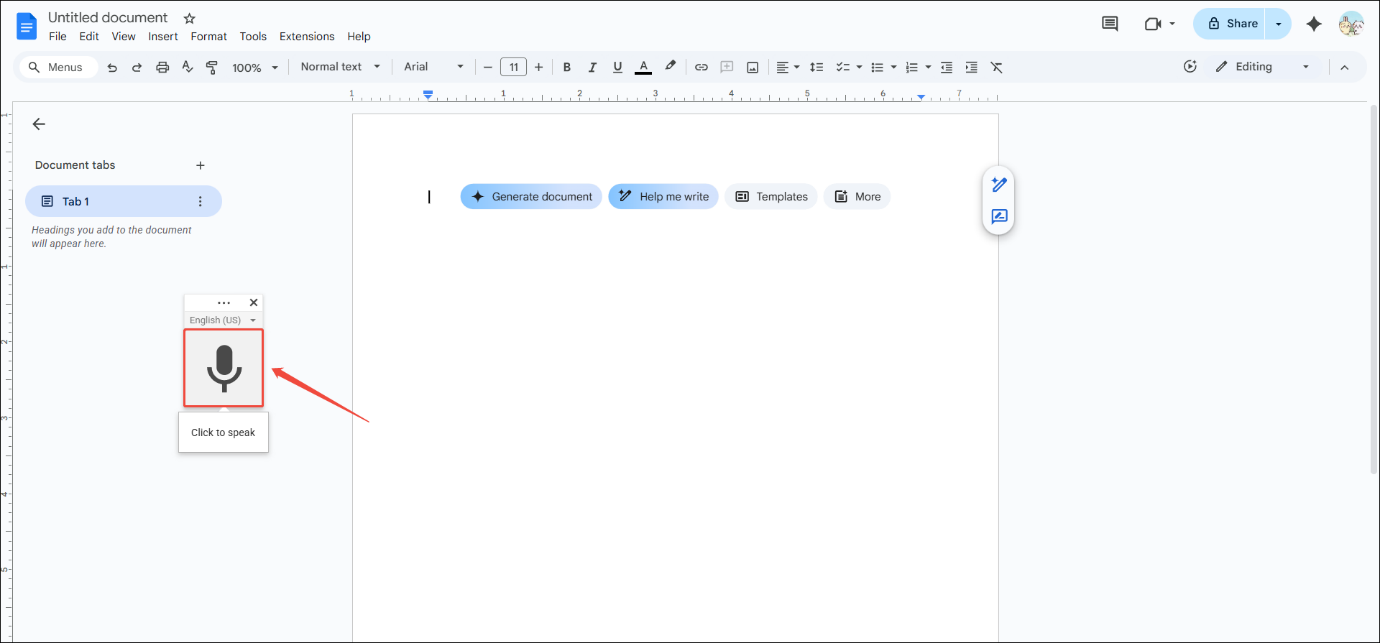
Step 5: Speak Closer to the Microphone
Speak into your microphone, and your words will be transcribed in real time and displayed on the blank document.
Step 6: Pause Recording and transcribing
After speaking, click the microphone icon again to pause transcription.
Google Docs Voice Typing feature only works for real-time speech transcription. If it’s pre-recorded audio, you need to hold the audio close to your microphone to play it for transcription. However, this results in poor audio quality in Google Docs, reducing accuracy. To transcribe audio recordings online, you can try using Otter.ai.
2. Otter.ai
Otter.ai is a web-based transcription tool. It can transcribe lectures, webinars, online courses, and more in real time. It can also identify speakers and generate summaries. What’s more, Otter.ai includes an AI chatbot. You can ask it questions or let it create content based on the transcribed text.
Here’s a quick guide on how to turn a speech to text using Otter:
Step 1: Go to Otter.ai Dashboard
Visit https://otter.ai/ on your desktop browser. Then, sign in with your Google, Microsoft, or Apple account.
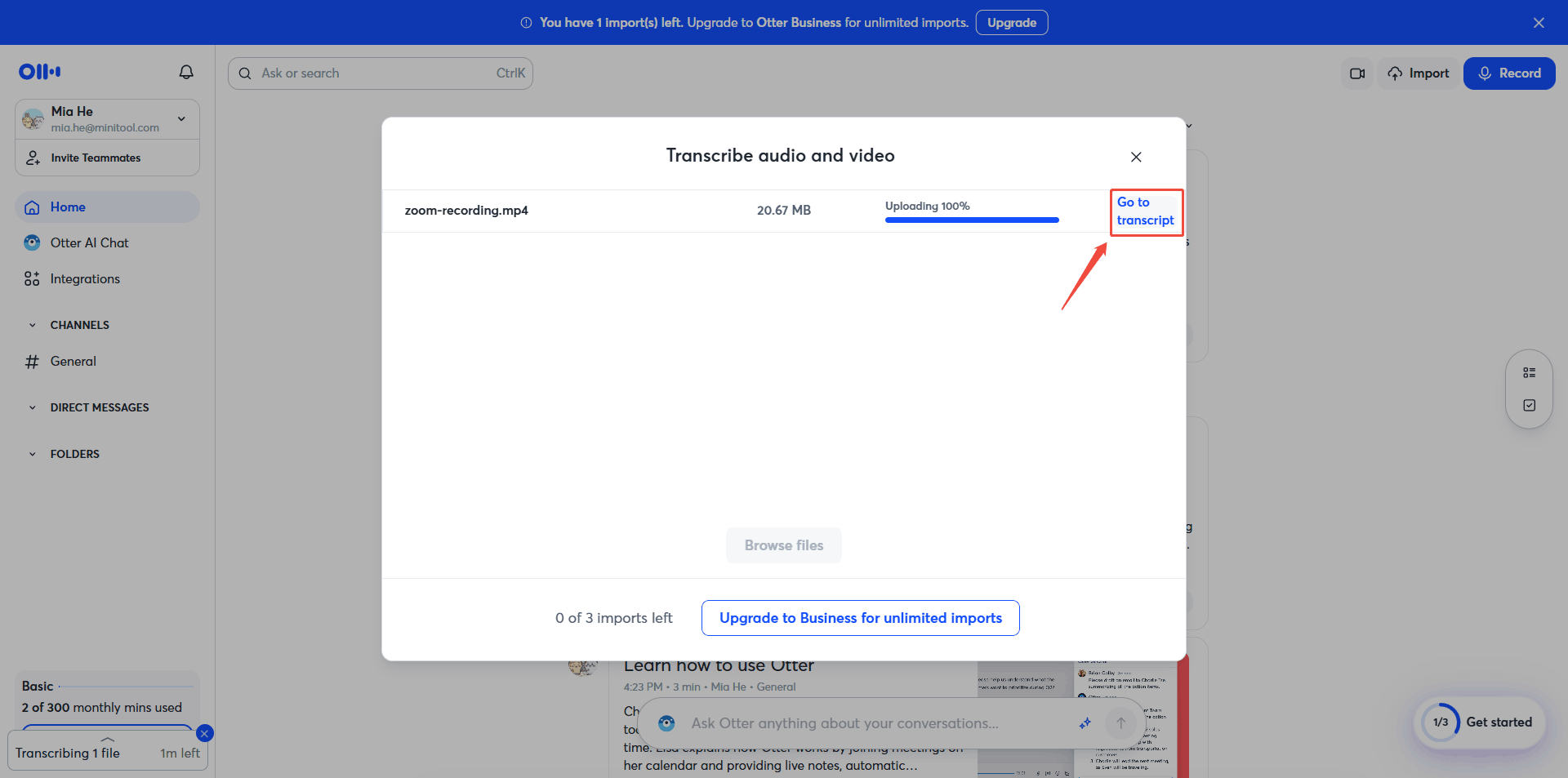
Step 2: Upload Your Audio
Click the Import button in the upper-right and click Browse files to add your audio recordings.
Step 3: Check the Transcript
Once the transcription is complete, click on Go to transcript to proofread the transcript.
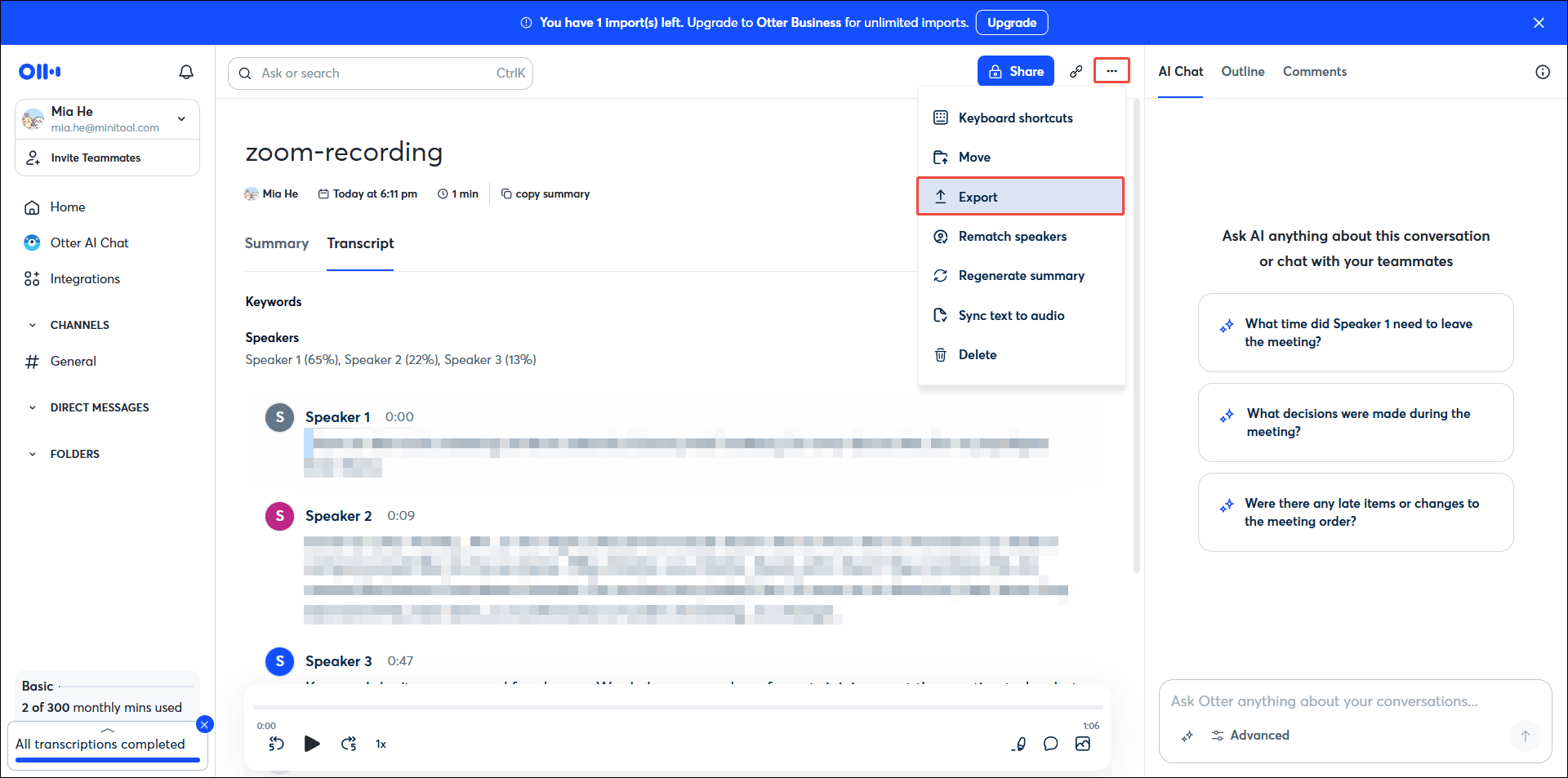
Step 4: Export the Transcript
Click the more icon in the upper-right corner, select Export, and choose a file format, like PDF, SRT, TXT, etc., and click on the Export button to save the transcript.
Otter.ai is an online speech recognition tool with many features. However, if you’re using the free version, you’ll have access to fewer features. For example, the video recording feature is only available for the expensive Enterprise plan.
How to Boost the Automatic Speech Recognition Accuracy
Improving speech recognition accuracy requires several factors, including audio quality and model training. Here are the details.
1. Improve Audio Quality
Audio quality is a crucial factor in the accuracy of speech recognition. Higher audio quality results in more accurate transcribed text. Although we cannot change the software itself, we can improve audio quality to improve the accuracy using the following methods.
#1 Use a High-Quality Microphone
First, make sure your microphone has good sound pickup. Using a high-quality microphone will allow for clearer vocals. This will also enable speech recognition software to clearly hear what you say.
#2 Speak Close to the Microphone
Your distance from the microphone will affect the volume. You need to speak close to the microphone, but not too close, to avoid audio distortion caused by pops and breaths.
#3 Reduce Background Noise
Please speak into the speech recognition tool in a quiet environment. If there is noise in the audio, please use noise reduction software, such as Audacity and Adobe Audition, to reduce the noise before transcription.
2. Improve Language Model
Low automatic speech recognition accuracy usually indicates a weak language model. Retraining with different speech data is the fastest way for developers to improve performance. This requires using diverse data, such as speech data from different languages, accents, and speaking styles, to train the language model. Inputting this broader range of data will significantly improve audio recognition accuracy.
Final Words
Automatic speech recognition has wide applications in daily life. This technology brings convenience and improves work efficiency and productivity. The three speech-to-text tools mentioned in this article are all based on ASR. Among them, MiniTool Video Converter, as an offline tool, is very suitable for video and audio transcription without an internet connection.
If you have encountered any problems when using MiniTool Video Converter, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us via [email protected], and we’ll get back to you fast.




User Comments :