If you usually need to record something with sound, you may have already been involved in recording mic and stereo mix together, which is good way to capture high-quality audio works. If you haven’t known this, read the below content offered by the free audio converter from MiniTool for more information.
In the world of audio recording, capturing sound faithfully and creatively is paramount. Whether you’re a musician, podcaster, filmmaker, or sound engineer, the tools you use to capture audio play a pivotal role in the final product’s quality. Two essential components in this realm are recording microphones and stereo mix techniques. Let’s delve into each and explore how they contribute to the art and science of recording.
Recording Microphones: The Sonic Architects
Recording microphones are the first link in the chain of capturing sound. These devices come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each tailored to specific recording scenarios. From the dynamic stage microphone to the sensitive condenser mic used in studio settings, the choice of microphone profoundly influences the character and fidelity of the recorded sound.
Dynamic Microphones
Known for their durability and versatility, dynamic microphones are commonly used in live performances and recording environments. They’re robust, capable of handling high sound pressure levels, making them ideal for capturing loud sound sources like guitar amplifiers and drums. Their relatively simple construction also makes them less sensitive to handling noise, making them a preferred choice for on-stage use.

Condenser Microphones
Engineered for capturing nuanced detail and sensitivity, condenser microphones excel in studio environments where precision and clarity are paramount. These microphones employ a diaphragm suspended near a backplate, creating a capacitor that changes its electrical charge in response to sound waves. This design results in more responsive and detailed audio capture, making condenser mics indispensable for recording vocals, acoustic instruments, and intricate soundscapes.

Ribbon Microphones
Characterized by their warm, vintage sound and delicate construction, ribbon microphones offer a unique sonic signature prized by many audio professionals. These mics utilize a thin strip of metal (the “ribbon”) suspended within a magnetic field to capture sound. While they may require careful handling and maintenance, ribbon microphones excel at reproducing smooth, natural tones, making them a favorite for recording brass instruments, strings, and vintage-style vocals.

Shotgun Microphones
Designed for directional recording, shotgun microphones excel in capturing sound from a specific direction while minimizing ambient noise. Their long, narrow pickup pattern makes them ideal for film and video production, allowing filmmakers to focus on specific dialogue or sound effects while rejecting unwanted noise from the surroundings.

Each type of microphone brings its own sonic characteristics and strengths to the table, allowing recording engineers and artists to sculpt the desired sound palette with precision and creativity.
Stereo Mix: Painting with Sound
Once the individual audio sources are captured, the next step is often to blend them together into a cohesive stereo mix. A stereo mix combines multiple audio tracks into a two-channel format, creating a spatial and immersive listening experience for the audience.
Panning
Panning refers to the placement of audio signals across the stereo field. By adjusting the pan controls, engineers can position sounds anywhere between the left and right speakers, creating a sense of space and dimensionality. This technique allows for the separation of instruments and vocals, giving each element its place in the sonic landscape.
Equalization (EQ)
EQ is used to shape the tonal balance of individual tracks within the mix. By boosting or cutting specific frequencies, engineers can enhance clarity, reduce muddiness, and highlight the unique characteristics of each sound source. EQ is a powerful tool for sculpting the overall sound of the mix, ensuring that each element occupies its own sonic space without clashing with others.
Compression
Compression is employed to control the dynamic range of audio signals, ensuring that loud and quiet passages are balanced and consistent. By reducing the dynamic range, engineers can make the mix sound more cohesive and polished, bringing out subtle details and enhancing overall clarity. Compression is particularly useful for smoothing out vocal performances, tightening up drum tracks, and adding punch to basslines.
Reverb and Effects
Reverb and other effects play a crucial role in creating a sense of depth and atmosphere within the mix. Reverb simulates the acoustic characteristics of physical spaces, adding lushness and dimension to dry recordings. Other effects, such as delay, chorus, and modulation, can be used to add movement, texture, and interest to individual tracks, enhancing the overall sonic palette of the mix.
By judiciously applying these techniques and tools, engineers can transform raw audio recordings into polished, professional-quality mixes that engage and captivate listeners.
Recording Mic and Stereo Mix with MiniTool Video Converter
MiniTool Video Converter has a built-in tool called Screen Recorder, which enables you to record both system sound and microphone. Let’s see how it works.
MiniTool Video ConverterClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1. Download, install, and launch MiniTool Video Converter on your Windows computer.
Step 2. Navigate to the Screen Record tab from the top menu.
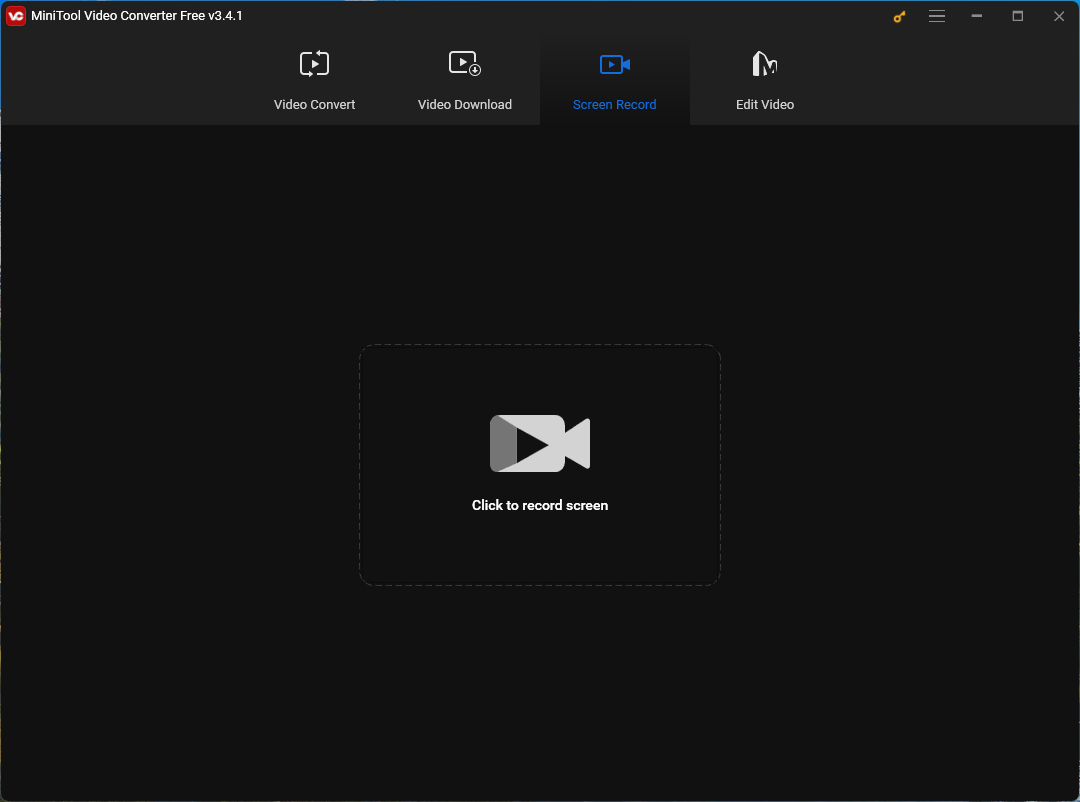
Step 3. Click the big recorder icon to trigger MiniTool Screen Recorder.
Step 4. Within MiniTool Screen Recorder, the system audio and microphone recording will be enabled by default.
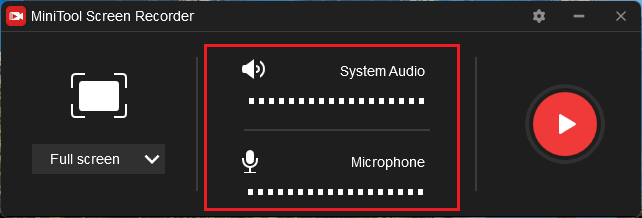
Step 5. Do other recording settings by clicking the Settings icon in the upper right.
Step 6. When all settings are done, click the big red Record icon to start recording.
Step 7. Stop recording by pressing the corresponding shortcut (F6 by default).
Conclusion
Recording microphones and stereo mix techniques are essential pillars of the audio recording process, each playing a unique and indispensable role in capturing and shaping sound. Whether you’re capturing the raw energy of a live performance or crafting intricate soundscapes in the studio, understanding these fundamental principles empowers you to unleash your creativity and realize your artistic vision. So, just pick up your microphone, fire up your mixing console, and let the magic of recording unfold.
Also Read



User Comments :